Dynamic Reflections Optimization
Dynamic reflections in the scene may significantly drop the performance if they aren't properly set up. For example, the planar reflection doubles the polygon count since it takes into account all geometry in the scene by default. It may raise performance issues in large and heavy scenes.
As an alternative, you can try to keep the number of reflections as low as possible. However, there is a way to optimize dynamic reflections usage without visual losses.
Using Reflection Masks#
The Reflection mask allows controlling rendering of dynamic reflections into the reflection camera viewport. This mask can be set for dynamic Environment Probes and planar reflections.
Optimizing planar reflections#
To optimize the scene with planar reflection probes, you can apply the following approach: set up the scene so that only the required planar reflections are rendered, and use less consuming Screen Space Reflections (SSR) for other reflections. An example workflow is as follows:
- Decide, which bit of the viewport mask would be responsible for reflection of the object.
- Open the Camera Settings window and enable the selected bit in the Reflection Viewport mask of the camera.
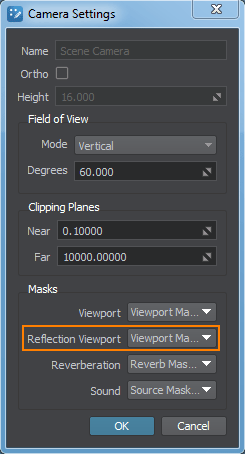
- In the Materials Hierarchy, select the reflective material and enable the same bit in the Reflection Viewport Mask in the Parameters tab of the Material Editor.
- In the World Hierarchy, select the node to be reflected and go to the Node tab of the Parameters window.
- In the Surfaces section, enable the selected bit in the Viewport Mask for all surfaces that should be reflected.
NoticeYou can create the special low-poly LOD surface that will be used for reflections only; the viewport mask of such a LOD shouldn't match the camera's viewport mask to exclude it from rendering.
- In the Materials Hierarchy, select the material of the node that should be reflected and enable the selected bit in the Viewport Mask in the Common tab of the Materials Editor.
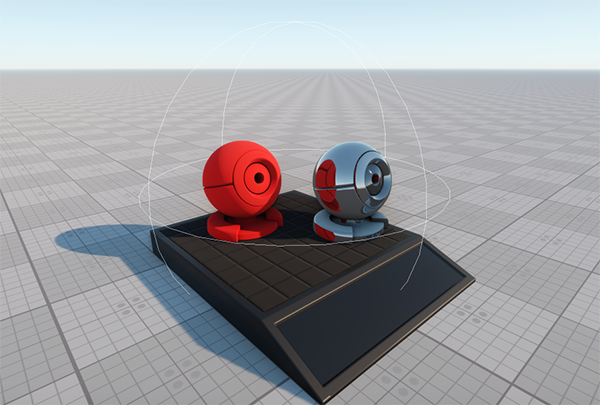
In the picture below, the reflection viewport mask of the plane has the same matching bit (or bits) with the camera reflection viewport mask and the Viewport masks of the red material ball and its material. The viewport masks of the other material balls don't have a matching bit with the reflection camera viewport mask and/or with the planar reflection viewport mask and, therefore, they aren't reflected:
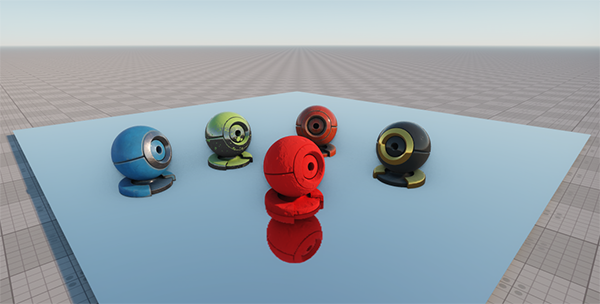 Masked planar reflection
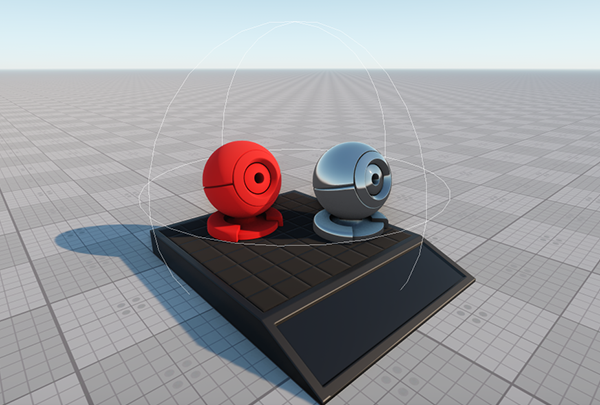
Masked planar reflection - Enable Screen Space Reflections to produce reflections of other nodes in the scene: on the Menu Bar, toggle the Rendering -> Features -> SSR option on.
NoticeThe SSR effect should be also enabled for the reflective material: go the Post Processing section of the States tab and check if the SSR option is enabled.
 Masked planar reflection + SSR
Masked planar reflection + SSR
Optimizing environment probe reflections#
Dynamic reflections provided by Environment Probes can be optimized in the same way as described above. To specify the Reflection Viewport mask for the Environment Probe, go to the Environment Probe section of the Parameters window and set the Reflection Viewport Mask parameter in the Baking Settings section.
In the left picture below, the reflection viewport mask of the Environment Probe matches the camera's Reflection Viewport mask and the Viewport masks of the red material ball and its material. In the right picture, the Reflection Viewport mask of the Environment Probe doesn't match the camera's Reflection Viewport mask:
 Content Optimization video tutorial.
Content Optimization video tutorial.Setting Up Reflection Distance#
One more method that allows optimizing rendering of dynamic reflections is to set the distance at which reflections are turned off.
Environment Probes#
This method is suitable for dynamic reflections provided by Environment Probes only.
- In the Menu Bar, choose Windows -> Settings and go to the Visibility Distances section of the Settings window that opens.
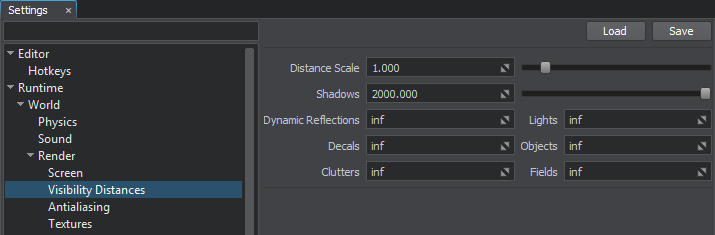
- For the Dynamic Reflections parameter, specify the distance from the camera, starting from which the reflections aren't rendered.
Planar Reflection Probes#
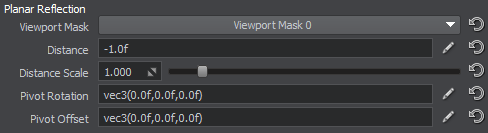
To optimize Planar Reflection Probe, you can try to adjust the following parameters of its material:
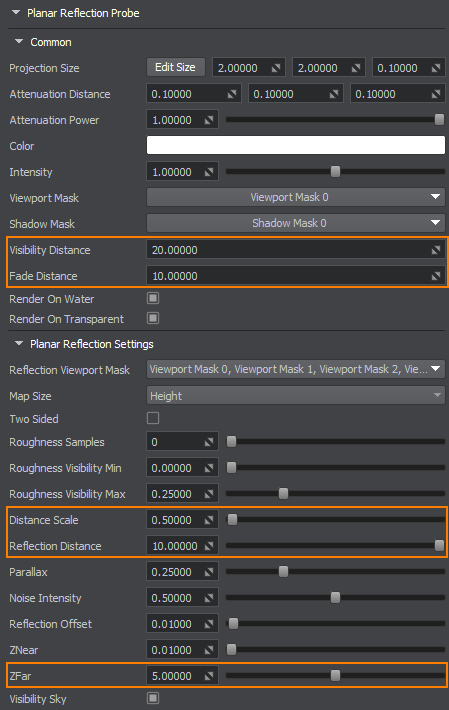
- Visibility and Fade distances not to render the reflecting surface at all, when the camera is far from it.
- Reflection Distance to avoid rendering reflections that can't be seen, when the camera is far from the reflecting surface.
- Distance Scale to apply the less detailed LODs to reflections at a closer distance, than to the corresponding reflected objects.
- ZFar to limit the viewing frustum that is used for reflection grabbing to avoid rendering reflections of unnesessary distant objects.