Краткий справочник по программированию
IntroductionВведение#
In the next chapters you will find the basic information on how to start programming 3D applications and videogames with UNIGINE. This FAQ consists of the following chapters:В настоящем справочнике вы найдете основную информацию о том, как начать программировать 3D-приложения и видеоигры с помощью UNIGINE. Справочник включает в себя следующие главы:
- Basic Scene Objects Основные объекты сцены
- Coordinate System Система координат
- Logging and Printing Messages to ConsoleВедение журнала и вывод сообщений в консоль
- Saving and Loading a World Сохранение и загрузка мира
- Closing the Application Закрытие приложения
- Creating and Deleting Nodes at Runtime Создание и удаление объектов во время выполнения
- Creating and Setting Up a Camera Создание и настройка камеры
- Creating and Setting up Light Sources Создание и настройка источников света
- Creating, Applying and Deleting Materials at Runtime Создание, применение и удаление материалов во время выполнения
- Managing Existing Scene Objects Управление существующими объектами сцены
- Performing Basic Transformations (Move, Rotate, Scale) Выполнение базовых преобразований (перемещение, поворот, масштабирование)
- Making the Game Process Framerate-independent Как сделать игровой процесс независимым от частоты кадров
- Managing Intersections Управление пересечениями
- Getting and Managing User Inputs Получение пользовательских вводов и управление ими
- Creating User Interface Создание пользовательского интерфейса
- Playing Sound and Music Воспроизведение звука и музыки
- Setting Up Physics Настройка физики
- Catching Nodes with World Triggers Обнаружение объектов с помощью World Trigger
Basic Scene ObjectsОсновные объекты сцены#
In terms of UNIGINE, node is a basic type from which all types of scene objects are inherited. Some of them appear visually: Objects, Decals, and Effects they all have surfaces to represent their geometry (mesh), while others (Light Sources, Players, etc.) are invisible.В UNIGINE нода (node) — это базовый тип, от которого наследуются все типы объектов сцены. Некоторые из них отображаются визуально: объекты, декали и эффекты — все они имеют поверхности для представления их геометрии (меш), в то время как другие ( Источники света, Персонажи и т.д.) невидимы.
Each node has a transformation matrix, which encodes position, rotation, and scale of the node in the world.Каждая нода имеет матрицу преобразования, которая кодирует положение, поворот и масштаб ноды в мире.
All scene objects added to the scene regardless of their type are called nodes.Все объекты сцены, добавленные в сцену, независимо от их типа, называются нодами.
Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on UNIGINE node types, see Built-in Node Types section.Дополнительные сведения о типах объектов UNIGINE см. в разделе Встроенные типы объектов.
- For more information on managing nodes via API, see Node-Related Classes section.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении нодами с помощью API см. раздел Node-классы.
Coordinate SystemСистема координат#
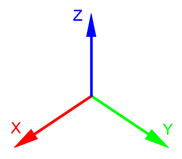
The 3D space in UNIGINE is represented by the right-handed Cartesian coordinate system: X and Y axes form a horizontal plane, Z axis points up. When exporting an animation from 3D editors, Y is considered a forward direction.Трехмерное пространство в UNIGINE представлено правой декартовой системой координат: оси X и Y образуют горизонтальную плоскость, ось Z направлена вверх. При экспорте анимации из 3D-редакторов Y считается прямым направлением.
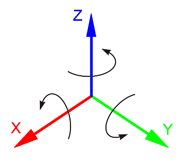
Positive rotation angle sets the rotation counterclockwise. It corresponds to the right-hand rule: if you set right hand thumb along the axis, other fingers wrapped will show rotation direction.Положительный угол поворота задает вращение против часовой стрелки. Это соответствует правилу правой руки: если вы установите большой палец правой руки вдоль оси, другие обернутые пальцы будут показывать направление вращения.
Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on UNIGINE node types, see Built-in Node Types section.Дополнительные сведения о типах объектов UNIGINE см. в разделе Встроенные типы объектов.
- For more information on managing nodes via API, see Node-Related Classes section.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении нодами с помощью API см. раздел Node-классы.
Logging and Printing Messages to ConsoleВедение журнала и вывод сообщений в консоль#
Printing messages to the log file and console helps to monitor overall progress of execution of your application and report errors which can be used in debugging. Log class makes it possible to print formatted string messages to the log file and the console. The code below demonstrates how to print various types of messages:Вывод сообщений в файл журнала и консоль помогает отслеживать общий ход выполнения вашего приложения и сообщать об ошибках, которые могут быть использованы при отладке. Класс Log позволяет печатать форматированные строковые сообщения в файл журнала и консоль. Приведенный ниже код демонстрирует, как выводить различные типы сообщений:
using namespace Unigine;
// auxiliary variables for messages
const char* file_name = "file.txt";
int ID = 10;
// reporting an error message
Log::error("Loading mesh: can't open \"%s\" file\n", file_name);
// reporting a message
Log::message("-> Added %d UI elements.\n", ID);
// reporting a warning message
Log::warning("ID of the \"%s\" file: %d.\n", file_name, ID);
// reporting a fatal error message to the log file and closing the application
Log::fatal("FATAL ERROR reading \"%s\" file!\n", file_name);Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
Saving and Loading a WorldСохранение и загрузка мира#
Some applications manage a single world, while other require several worlds to be managed. In any case, it is very useful to know how to save our current world and load some other. In order to solve this task, we should use the World class, which is designed as a singleton.Некоторые приложения управляют одним миром, в то время как другие требуют управления несколькими мирами. В любом случае, очень полезно знать, как сохранить наш текущий мир и загрузить какой-нибудь другой. Чтобы решить эту задачу, мы должны использовать класс World, который разработан как синглтон.
#include <UnigineWorld.h>
using namespace Unigine;
/* .. */
// loading world from the my_world.world file
World::loadWorld("my_world");We can also do the same via the console by using the Console class, which is also designed as a singleton.Мы также можем сделать то же самое через консоль, используя класс Console, который также разработан как синглтон.
#include <UnigineConsole.h>
using namespace Unigine;
/* .. */
// saving current world to the my_world.world file
Console::run("world_save my_world");
// loading world from the my_world.world file
Console::run("world_load my_world");Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on managing worlds via API, see the World class article.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении мирами с помощью API см. статью о классе World.
- For more information on the console and available commands, see Console article.Для получения дополнительной информации о консоли и доступных командах см. статью Консоль.
- For more information on managing the console via API, see Console class article.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении консолью через API см. статью о классе Console.
- For more information on managing world nodes that are to be saved via API, see the methods of the Node class.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении мировыми нодами, которые должны быть сохранены с помощью API, см. методы класса Node.
Closing the ApplicationЗакрытие приложения#
Any application needs to be closed at some moment. To close your application you should use the Engine class.Любое приложение должно быть закрыто в какой-то момент. Чтобы закрыть ваше приложение, используйте класс Engine.
To close the application the following code is to be used:Чтобы закрыть приложение, необходимо использовать следующий код:
using namespace Unigine;
/* .. */
// closing the application
Engine::get()->quit();Creating and Deleting Nodes at RuntimeСоздание и удаление нод во время выполнения#
Nodes can be created and deleted at runtime almost as easy as in the Editor. The basic set of actions is as follows:Ноды можно создавать и удалять во время выполнения почти так же просто, как в редакторе. Основной набор действий заключается в следующем:
- Creation. To create a node we should declare a smart pointer for the type of the node we are going to create and call a constructor of the corresponding class providing construction parameters if necessary. Создание. Чтобы создать ноду, мы должны объявить интеллектуальный указатель для типа ноды, которую мы собираемся создать, и вызвать конструктор соответствующего класса, при необходимости предоставляя параметры построения.
- Deletion. To delete a node we simply call the deleteLater() method for the node we are going to remove. Удаление. Чтобы удалить ноду, мы просто вызываем метод deleteLater() для ноды, которую мы собираемся удалить.
// creating a node of the NodeType named nodename
<NodeType>Ptr nodename = <NodeType>::create(<construction_parameters>);
// removing the node
nodename.deleteLater();Now let us illustrate the process of creating and deleting a node using a simple static mesh (ObjectMeshStatic) by both creating a box surface and loading a mesh from an asset as an example.Теперь давайте проиллюстрируем процесс создания и удаления ноды с использованием простого статического меша (ObjectMeshStatic), создав поверхность поля и загрузив меш из ассета в качестве примера.
int AppWorldLogic::init()
{
// first, we're creating a mesh instance as it is required to call an ObjectMeshStatic constructor
MeshPtr mesh = Mesh::create();
// loading a mesh from an fbx model imported to the data/fbx/ folder using the Editor
mesh -> load("fbx/model.fbx/model.mesh");
// creating a box surface with a given size to the mesh
mesh -> addBoxSurface("box_surface", Math::vec3(0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f));
//create an ObjectMeshStatic node
ObjectMeshStaticPtr my_object = ObjectMeshStatic::create(mesh);
// removing the node
my_object.deleteLater();
// clearing the mesh
mesh.clear();
return 1;
}Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- You can create primitives via code using the Primitives class.Вы можете создавать примитивы с помощью кода, используя класс Primitives.
- For more information on managing world nodes, see the methods of the Node class.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении мировыми нодами см. методы класса Node.
Creating and Setting Up a CameraСоздание и настройка камеры#
A camera is a viewport to the world, without it you actually won't be able to see anything. Cameras in UNIGINE are managed using players. When you add a new player, it creates a camera and specifies controls, masks, postprocess materials for this camera. Камера — это окно в мир, без него вы на самом деле ничего не сможете увидеть. Камеры в UNIGINE управляются с помощью Player. Когда вы добавляете нового персонажа, он создает камеру и задает элементы управления, маски, материалы для последующей обработки для этой камеры.
In order to set a new player as active one we should use the Game class which is designed as a singleton.Для того, чтобы установить нового персонажа в качестве активного, мы должны использовать класс Game, который разработан как синглтон.
The following code illustrates creation of a PlayerSpectator and setting it as the active game camera.Следующий код иллюстрирует создание PlayerSpectator и установку его в качестве активной игровой камеры.
#include <UnigineGame.h>
// injecting Unigine namespace to the global namespace
using namespace Unigine;
int AppWorldLogic::init()
{
// creating a new PlayerSpectator instance
PlayerSpectatorPtr playerSpectator = PlayerSpectator::create();
// setting necessary parameters: FOV, ZNear, ZFar, view direction vector and position.
playerSpectator->setFov(90.0f);
playerSpectator->setZNear(0.1f);
playerSpectator->setZFar(10000.0f);
playerSpectator->setViewDirection(Math::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f));
playerSpectator->setWorldPosition(Math::Vec3(-1.6f, -1.7f, 1.7f));
// setting the player as a default one via the Game singleton instance
Game::setPlayer(playerSpectator);
return 1;
}Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on players, see the Players article.Для получения дополнительной информации об игроках см. статью Персонажи.
- For more information on players API, see the Players-Related Classes article.Для получения дополнительной информации об API игроков см. статью Player-классы.
- For more information on the Game class, see the Game class article.Для получения дополнительной информации о игровом классе см. статью о классе Game.
Creating and Setting up Light SourcesСоздание и настройка источников света#
Lighting is the basis of every scene defining colors and final look of your objects. Lights in UNIGINE are created the same way as all nodes. Освещение является основой каждой сцены, определяющей цвета и окончательный вид ваших объектов. Источники света в UNIGINE создаются так же, как и все остальные ноды.
Let us consider creation of a world light source as an example:Давайте рассмотрим создание мирового источника света в качестве примера:
#include <UnigineLights.h>
// injecting Unigine namespace to the global namespace
using namespace Unigine;
int AppWorldLogic::init()
{
// creating a world light source and setting its color to white
LightWorldPtr sun = LightWorld::create(Math::vec4(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f));
// setting light source's parameters (intensity, disable angle, scattering type, name and rotation)
sun->setName("Sun");
sun->setDisableAngle(90.0f);
sun->setIntensity(1.0f);
sun->setScattering(LightWorld::SCATTERING::SCATTERING_SUN);
sun->setWorldRotation(Math::quat(86.0f, 30.0f, 300.0f));
return 1;
}Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on light sources, see the Light sources article.Для получения дополнительной информации об источниках света см. статью Источники света.
- For more information on light sources API, see the Lights-Related Classes article.Для получения дополнительной информации об API источников света см. статью Lights-классы.
Creating, Applying and Deleting Materials at RuntimeСоздание, применение и удаление материалов во время выполнения#
Materials assigned to particular surfaces of a node determine how the node is to be rendered. They implement the shaders and control what options, states, parameters of different types and textures are used to render the node during the rendering passes. To manage materials we use the following two classes: Материалы, назначенные определенным поверхностям объекта, определяют, как будет отображаться объект. Они реализуют шейдеры и управляют тем, какие опции, состояния, параметры различных типов и текстуры используются для рендеринга объекта во время прохода рендеринга. Для управления материалами мы используем следующие два класса:
- Materials class which represents an interface for managing loaded materials.Класс Materials, который представляет интерфейс для управления загруженными материалами.
- Material class which is used to manage each individual material.Класс Material, который используется для управления каждым отдельным материалом.
The following code can be used to create a new material inherited from the mesh_base material.Следующий код можно использовать для создания нового материала, унаследованного от материала mesh_base.
#include <UnigineMaterials.h>
// injecting Unigine namespace to the global namespace
using namespace Unigine;
int AppWorldLogic::init()
{
// creating a box (ObjectMeshDynamic node)
MeshPtr mesh = Mesh::create();
mesh->addBoxSurface("box_surface", Math::vec3(1.5f, 1.5f, 1.5f));
ObjectMeshDynamicPtr my_mesh = ObjectMeshDynamic::create(mesh);
// getting the base mesh_base material to inherit from
MaterialPtr mesh_base = Materials::findManualMaterial("Unigine::mesh_base");
// inherit a new child material from it
MaterialPtr my_mesh_base = mesh_base->inherit();
// save it to "materials/my_mesh_base0.mat"
my_mesh_base->createMaterialFile("materials/my_mesh_base0.mat");
// setting the albedo color of the material to red
my_mesh_base->setParameterFloat4("albedo_color", Math::vec4(255, 0, 0, 255));
// assigning a "my_mesh_base0.mat" material to the surface 0 of the my_mesh ObjectMeshDynamic node
my_mesh->setMaterialPath("materials/my_mesh_base0.mat", 0);
// assigning a "my_mesh_base0.mat" material to all surfaces of the my_mesh ObjectMeshDynamic node
my_mesh->setMaterialPath("materials/my_mesh_base0.mat", "*");
return 1;
}
int AppWorldLogic::shutdown()
{
// deleting the material "materials/my_mesh_base0.mat"
Materials::removeMaterial(Materials::findMaterialByPath("materials/my_mesh_base0.mat")->getGUID());
return 1;
}Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on creating and editing materials via API, see the Material class article.Для получения дополнительной информации о создании и редактировании материалов с помощью API см. статью о классе Material.
- For more information on managing loaded materials via API, see the Materials class article.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении загруженными материалами с помощью API см. статью о классе Materials.
- For more information on materials files formats, see the Materials Files section.Для получения дополнительной информации о форматах файлов материалов см. раздел Файлы материалов.
- For more information on materials parameters, see the materials files in the %UNIGINE_SDK_BROWSER_INSTALLATION_FOLDER%/sdks/%CURRENT_SDK%/data/core/materials/default/ folder.Для получения дополнительной информации о параметрах материалов см. файлы материалов в папке %UNIGINE_SDK_BROWSER_INSTALLATION_FOLDER%/sdks/%CURRENT_SDK%/data/core/materials/default/.
Managing Existing Scene ObjectsУправление существующими объектами сцены#
Not all content in the world is created at runtime, so we should be able to operate with nodes that already exist. How do we get pointers to existing objects in order to manage them? This is where the World class comes into play again. Basically, there are two ways we can get a pointer to a certain node using the methods of the World class:Не весь контент в мире создается во время выполнения, поэтому мы должны иметь возможность работать с уже существующими нодами. Как мы получаем указатели на существующие объекты, чтобы управлять ими? Здесь снова вступает в игру класс World. В принципе, есть два способа, которыми мы можем получить указатель на определенноу ноду, используя методы класса World:
- getNodeByName() method - when we know node's nameметод getNodeByName() — когда мы знаем имя ноды
- getNodeByID() method - when we know the node's IDметод getNodeByID() — когда мы знаем идентификатор ноды
These methods return a NodePtr value, which is a pointer to the base class, but in order to perform operations with a certain object (e.g. ObjectMeshDynamicPtr) we need to perform downcasting (i.e. convert from a pointer-to-base to a pointer-to-derived).Эти методы возвращают значение NodePtr, которое является указателем на базовый класс, но для выполнения операций с определенным объектом (например, ObjectMeshDynamicPtr) нам необходимо выполнить понижающее преобразование (т.е. преобразовать указатель на базовый класс в указатель на производный).
Sometimes you may also need to perform upcasting (i.e. convert from a pointer-to-derived to a pointer-to-base), in this case you can use the derived class itself. The code below demonstrates the points described above.Иногда вам также может потребоваться выполнить upcasting (т.е. преобразовать указатель на производный в указатель на базовый), в этом случае вы можете использовать сам производный класс. Приведенный ниже код демонстрирует моменты, описанные выше.
#include <UnigineWorld.h>
using namespace Unigine;
/* .. */
// find a pointer to node by a given name
NodePtr baseptr = World::getNodeByName("my_meshdynamic");
// cast a pointer-to-derived from pointer-to-base with automatic type checking
ObjectMeshDynamicPtr derivedptr = checked_ptr_cast<ObjectMeshDynamic>(baseptr);
// static cast (pointer-to-derived from pointer-to-base)
ObjectMeshDynamicPtr derivedptr = static_ptr_cast<ObjectMeshDynamic>(World::getNodeByName("my_meshdynamic"));
// upcast to the pointer to the Object class which is a base class for ObjectMeshDynamic
ObjectPtr object = derivedptr;
// upcast to the pointer to the Node class which is a base class for all scene objects
NodePtr node = derivedptr;There are the following ways to get a component from a node:Существуют следующие способы получения компонента для ноды:
// get the component assigned to a node by type "MyComponent"
MyComponent* my_component = ComponentBase::getComponent<MyComponent>(node);
// // do the same by using the function of the Component System
MyComponent* my_component = ComponentSystem::get()->getComponent<MyComponent>(color_zone);Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on working managing smart pointers, see the Working with Smart Pointers article.Дополнительные сведения о работе с умными указателями см. в статье Работа с умными указателями.
- For more information see the World class article.Для получения дополнительной информации см. статью о классе World.
Performing Basic Transformations (Move, Rotate, Scale)Выполнение базовых преобразований (перемещение, поворот, масштабирование)#
Every node has a transformation matrix, which encodes position, rotation, and scale of the node in the world. If a node is added as a child of another node, it has a transformation matrix that is related to its parent node. That is why the Node class has different functions: getTransform(), setTransform() and getWorldTransform(), setWorldTransform() that operate with local and world transformation matrices respectively. The following code illustrates how to perform basic node transformations:Каждая нода имеет матрицу преобразования, которая кодирует положение, поворот и масштаб ноды в мире. Если нода добавляется как дочерняя для другой ноды, она имеет матрицу преобразования, связанную с ее родительской нодой. Вот почему класс Node имеет разные функции: getTransform(), setTransform() и getWorldTransform(), setWorldTransform(), которые работают с локальными и мировыми матрицами преобразования соответственно. Следующий код иллюстрирует, как выполнять базовые преобразования нод:
// injecting Unigine namespace to the global namespace
using namespace Unigine;
using namespace Unigine::Math;
// move the node by X, Y, Z units along the corresponding axes
node->setWorldPosition(node->getWorldPosition() + Vec3(X, Y, Z));
// move the node by one unit along the Y axis
node->worldTranslate(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
// rotate the node around the axis (X, Y, Z) by the Alpha angle
node->setWorldRotation(node->getWorldRotation() * quat(Vec3(X, Y, Z), Alpha));
// rotate the node around X, Y, and Z axes by the corresponding angle (angle_X, angle_Y, angle_Z)
node->setWorldRotation(node->getWorldRotation() * quat(angle_X, angle_Y, angle_Z));
// rotate the node by 45 degrees along the Z axis
node->worldRotate(0.0f, 0.0f, 45.0f);
// orient the node using a direction vector and a vector pointing upwards
node->setWorldDirection(vec3(0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f), vec3_up, AXIS_Y);
// setting node scale to Scale_X, Scale_Y, Scale_Z along the corresponding axes
node->setWorldScale(vec3(Scale_X, Scale_Y, Scale_Z));
// setting new transformation matrix to scale the node 2 times along all axes, rotate it by 45 degrees around the Z-axis and move it by 1 unit along all axes
Mat4 transform = Mat4(translate(vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f)) * rotate(quat(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 45.0f)) * scale(vec3(2.0f)));
// setting node transformation matrix relative to its parent
node->setTransform(transform);
// setting node transformation matrix relative to the world origin
node->setWorldTransform(transform);Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on matrix transformations, see the Matrix Transformations article.Для получения дополнительной информации о матричных преобразованиях см. статью Матричные преобразования.
Making the Game Process Framerate-independentСделать игровой процесс независимым от частоты кадров#
As the frame rate of our application may vary (i.e. the AppWorldLogic::update() method will be called more or less frequently) depending on hardware, we should do something to ensure that certain actions are performed at the same time periods regardless of the frame rate (e.g. change something once per second etc). To make your game frame rate independent you can use a scaling multiplier (the time in seconds it took to complete the last frame) returned by the following methods:Поскольку частота кадров нашего приложения может варьироваться (т.е. метод AppWorldLogic::update() будет вызываться более или менее часто) в зависимости от аппаратного обеспечения, мы должны что-то сделать, чтобы гарантировать, что определенные действия выполняются в одни и те же периоды времени независимо от частоты кадров (например, изменять что-то один раз в секунду и т.д.). Чтобы сделать частоту кадров вашей игры независимой, вы можете использовать множитель масштабирования (время в секундах, затраченное на завершение последнего кадра), возвращаемый следующими методами:
- Engine::getIfps() returns the inverse FPS value for your application.Engine::getIfps() возвращает обратное значение FPS для вашего приложения.
- Game::getIfps() returns the scaled inverse FPS value. This class is to be used when you want to speed up, slow down or pause rendering, physics or game logic.Game::getIfps() возвращает масштабированное обратное значение FPS. Этот класс предназначен для использования, когда вы хотите ускорить, замедлить или приостановить рендеринг, физику или игровую логику.
To change the transformations you can use the following code:Чтобы изменить преобразования, вы можете использовать следующий код:
#include <UnigineGame.h>
// injecting Unigine namespace to the global namespace
using namespace Unigine;
int AppWorldLogic::update()
{
// getting an inverse FPS value (the time in seconds it took to complete the last frame)
float ifps = Game::getIFps();
// moving the node up by 0.3 units every second instead of every frame
node->worldTranslate(Math::Vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.3f * ifps));
return 1;
}To perform some changes once in a certain period of time you can use the following code:Чтобы выполнить некоторые изменения один раз за определенный промежуток времени, вы можете использовать следующий код:
#include <UnigineGame.h>
// injecting Unigine namespace to the global namespace
using namespace Unigine;
const float INTERVAL_DURATION = 5; // interval duration
float elapsed_time = INTERVAL_DURATION; // current time left to make changes
int AppWorldLogic::update()
{
// getting an inverse FPS value (the time in seconds it took to complete the last frame)
float ifps = Game::getIFps();
// checking if it's time to make changes
if (elapsed_time < 0.0f)
{
/* .. DO SOME CHANGES .. */
// resetting elapsed time counter
elapsed_time = INTERVAL_DURATION;
}
// decreasing elapsed time counter
elapsed_time -= ifps;
return 1;
}Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
Managing IntersectionsУправление пересечениями#
Intersections are widely used in 3D applications. In UNIGINE there are three main types of intersections: Пересечения широко используются в 3D-приложениях. В UNIGINE существует три основных типа пересечений:
- World intersection - an intersection with objects and nodes. World Intersection — пересечение с объектами и нодами.
- Physics intersection - an intersection with shapes and collision objects. Physics Intersection — пересечение с формами и коллизионными объектами.
- Game intersection - an intersection with pathfinding nodes like obstacles. Game Intersection — пересечение с нодами поиска пути, такими как препятствия.
But there are some conditions to detect intersections with the surface: Но есть некоторые условия для обнаружения пересечений с поверхностью:
- The surface is enabled.Поверхность включена.
- The surface has a material assigned.Поверхности присвоен материал.
Per-surface Intersection flag is enabled.Для каждой поверхности включен флаг Intersection.
ПримечаниеYou can set this flag to the object's surface by using the Object.setIntersection() function.Вы можете установить этот флаг на поверхность объекта с помощью функции Object.setIntersection().
The code below illustrates several ways of using world intersections:Приведенный ниже код иллюстрирует несколько способов использования мировых пересечений:
- to find all nodes intersected by a bounding boxчтобы найти все ноды, пересекаемые ограничивающим прямоугольником;
- to find all nodes intersected by a bounding sphereчтобы найти все ноды, пересекаемые ограничивающей сферой;
- to find all nodes intersected by a bounding frustumчтобы найти все ноды, пересекаемые ограничивающим усеченным конусом;
- to find the first object intersected by a rayчтобы найти первый объект, пересеченный лучом.
#include <UnigineGame.h>
#include <UnigineWorld.h>
// injecting Unigine namespace to the global namespace
using namespace Unigine;
int listNodes(Vector<Ptr<Node>>& nodes, const char* intersection_with)
{
Log::message("Total number of nodes intersecting a %s is: %i \n", intersection_with, nodes.size());
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++)
{
Log::message("Intersected node: %s \n", nodes.get(i)->getName());
}
// clearing the list of nodes
nodes.clear();
return 1;
}
int AppWorldLogic::update()
{
// getting a player pointer
PlayerPtr player = Game::getPlayer();
// creating a vector to store intersected nodes
Vector<Ptr<Node>> nodes;
//-------------------------- FINDING INTERSECTIONS WITH A BOUNDING BOX -------------------------
// initializing a bounding box with a size of 3 units, located at the World's origin
WorldBoundBox boundBox(Math::Vec3(0.0f), Math::Vec3(3.0f));
// finding nodes intersecting a bounding box and listing them if any
if (World::getIntersection(boundBox, nodes))
listNodes(nodes, "bounding box");
//------------------------- FINDING INTERSECTIONS WITH A BOUNDING SPHERE ------------------------
// initializing a bounding sphere with a radius of 3 units, located at the World's origin
WorldBoundSphere boundSphere(Math::Vec3(0.0f), 3.0f);
// finding nodes intersecting a bounding sphere and listing them if any
if (World::getIntersection(boundSphere, nodes))
listNodes(nodes, "bounding sphere");
//------------------------- FINDING INTERSECTIONS WITH A BOUNDING FRUSTUM -----------------------
// initializing a bounding frustum with a frustum of the player's camera
WorldBoundFrustum boundFrustum(player->getCamera()->getProjection(), player->getCamera()->getModelview());
// finding ObjectMeshStaticNodes intersecting a bounding frustum and listing them if any
if (World::getIntersection(boundFrustum, Node::OBJECT_MESH_STATIC, nodes))
listNodes(nodes, "bounding frustum");
//---------------- FINDING THE FIRST OBJECT INTERSECTED BY A RAY CAST FROM P0 to P1 --------------
// initializing points of the ray from player's position in the direction pointed by the mouse cursor
Math::ivec2 mouse = Input::getMousePosition();
Math::Vec3 p0 = player->getWorldPosition();
Math::Vec3 p1 = p0 + Math::Vec3(player->getDirectionFromMainWindow(mouse.x, mouse.y)) * 100;
//creating a WorldIntersection object to store the information about the intersection
WorldIntersectionPtr intersection = WorldIntersection::create();
// casting a ray from p0 to p1 to find the first intersected object
ObjectPtr obj = World::getIntersection(p0, p1, 1, intersection);
// print the name of the first intersected object and coordinates of intersection point if any
if (obj)
{
Math::Vec3 p = intersection->getPoint();
Log::message("The first object intersected by the ray at point (%f, %f, %f) is: %s \n ", p.x, p.y, p.z, obj->getName());
}
return 1;
}Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on intersections, see the Intersections article.Для получения дополнительной информации о пересечениях см. статью Пересечения.
- For more information on managing World intersections via API, see the World class article.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении пересечениями World с помощью API см. статью о классе World.
- For more information on managing Game intersections via API, see the Game class article.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении пересечениями Game с помощью API см. статью о классе Game.
- For more information on managing Physics intersections via API, see the Physics class article.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении пересечениями Physics с помощью API см. статью о классе Physics.
Getting and Managing User InputsПолучение пользовательских данных и управление ими#
The majority of applications are designed to interact with the user. In UNIGINE you can manage user inputs using the following classes:Большинство приложений предназначены для взаимодействия с пользователем. В UNIGINE вы можете управлять вводимыми пользовательскими данными, используя следующие классы:
- Класс Input
- Класс Controls
- Класс ControlsApp
The following code illustrates how to use Input class to get mouse coordinates in case if a right mouse button was clicked and to close the application if "q" key was pressed (ignoring this key if the console is opened):Следующий код иллюстрирует, как использовать класс Input для получения координат мыши в случае, если была нажата правая кнопка мыши, и для закрытия приложения, если была нажата клавиша "q" (игнорируя эту клавишу, если консоль открыта):
#include <UnigineInput.h>
#include <UnigineConsole.h>
int AppWorldLogic::update()
{
// if right mouse button is clicked
if (Input::isMouseButtonDown(Input::MOUSE_BUTTON_RIGHT))
{
Math::ivec2 mouse = Input::getMousePosition();
// report mouse cursor coordinates to the console
Log::message("Right mouse button was clicked at (%d, %d)\n", mouse.x, mouse.y);
}
// closing the application if a 'Q' key is pressed, ignoring the key if the console is opened
if (Input::isKeyDown(Input::KEY_Q) && !Console::isActive())
{
Engine::get()->quit();
}
return 1;
}The following code illustrates how to use Controls class to handle keyboard input:Следующий код иллюстрирует, как использовать класс Controls для обработки ввода с клавиатуры:
#include <UnigineGame.h>
int AppWorldLogic::update()
{
// getting current controls
ControlsPtr controls = Game::getPlayer()->getControls();
// checking controls states and reporting which buttons were pressed
if (controls->clearState(Controls::STATE_FORWARD) || controls->clearState(Controls::STATE_TURN_UP))
{
Log::message("FORWARD or UP key pressed\n");
}
else if (controls->clearState(Controls::STATE_BACKWARD) || controls->clearState(Controls::STATE_TURN_DOWN))
{
Log::message("BACKWARD or DOWN key pressed\n");
}
else if (controls->clearState(Controls::STATE_MOVE_LEFT) || controls->clearState(Controls::STATE_TURN_LEFT))
{
Log::message("MOVE_LEFT or TURN_LEFT key pressed\n");
}
else if (controls->clearState(Controls::STATE_MOVE_RIGHT) || controls->clearState(Controls::STATE_TURN_RIGHT))
{
Log::message("MOVE_RIGHT or TURN_RIGHT key pressed\n");
}
return 1;
}The following code illustrates how to use ControlsApp class to map keys and buttons to states and then to handle user input:Следующий код иллюстрирует, как использовать класс ControlsApp для сопоставления клавиш и кнопок с состояниями, а затем для обработки пользовательского ввода:
#include <UnigineGame.h>
int AppWorldLogic::init()
{
// remapping states to other keys and buttons
ControlsApp::setStateKey(Controls::STATE_FORWARD, Input::KEY_PGUP);
ControlsApp::setStateKey(Controls::STATE_BACKWARD, Input::KEY_PGDOWN);
ControlsApp::setStateKey(Controls::STATE_MOVE_LEFT, Input::KEY_L);
ControlsApp::setStateKey(Controls::STATE_MOVE_RIGHT, Input::KEY_R);
ControlsApp::setStateMouseButton(Controls::STATE_JUMP, Input::MOUSE_BUTTON_LEFT);
return 1;
}
int AppWorldLogic::update()
{
if (ControlsApp::clearState(Controls::STATE_FORWARD))
{
Log::message("FORWARD key pressed\n");
}
else if (ControlsApp::clearState(Controls::STATE_BACKWARD))
{
Log::message("BACKWARD key pressed\n");
}
else if (ControlsApp::clearState(Controls::STATE_MOVE_LEFT))
{
Log::message("MOVE_LEFT key pressed\n");
}
else if (ControlsApp::clearState(Controls::STATE_MOVE_RIGHT))
{
Log::message("MOVE_RIGHT key pressed\n");
}
else if (ControlsApp::clearState(Controls::STATE_JUMP))
{
Log::message("JUMP button pressed\n");
}
return 1;
}Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on managing user inputs using Input class, see the Input class article.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении пользовательскими вводами с помощью класса Input см. статью Input class.
- For more information on managing user inputs using Controls class, see the Controls class article.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении пользовательскими вводами с помощью класса Controls см. статью Controls class.
- For more information on managing user inputs using ControlsApp class, see the ControlsApp class article.Для получения дополнительной информации об управлении пользовательскими вводами с помощью класса ControlsApp см. статью ControlsApp class.
Creating User InterfaceСоздание пользовательского интерфейса#
In UNIGINE a Graphical User Interface (GUI) is composed of different types of widgets added to it. Basically, there are two ways of creating GUI:В UNIGINE графический пользовательский интерфейс (GUI) состоит из различных типов виджетов, добавленных к нему. В принципе, существует два способа создания графического интерфейса:
- By adding widgets to the system GUI (Unigine user interface) that is rendered on top of application window.Путем добавления виджетов в системный графический интерфейс (пользовательский интерфейс UNIGINE), который отображается поверх окна приложения.
- By adding widgets to a GUI object positioned in the world. In this case, any postprocessing filter can be applied.Путем добавления виджетов к объекту GUI, расположенному в мире. В этом случае может быть применен любой фильтр постобработки.
To add elements to the system GUI you should use the Gui class.Чтобы добавить элементы в системный графический интерфейс, вы должны использовать класс Gui.
There are 2 ways to create the GUI layout:Существует 2 способа создания макета графического интерфейса:
- Directly from the code via GUI-related classesНепосредственно из кода через GUI-классы
- By using User interface (UI) filesС помощью Файлов пользовательского интерфейса (UI)
The following code demonstrates how to add a label and a slider to the system GUI:Следующий код демонстрирует, как добавить метку и ползунок в системный графический интерфейс:
#include <UnigineUserInterface.h>
// injecting Unigine namespace to the global namespace
using namespace Unigine;
GuiPtr gui;
int AppWorldLogic::init()
{
// getting a GUI pointer
gui = Gui::getCurrent();
// creating a label widget and setting up its parameters
WidgetLabelPtr widget_label = WidgetLabel::create(gui, "Label text:");
widget_label->setToolTip("This is my label!");
widget_label->arrange();
widget_label->setPosition(10, 10);
// creating a slider widget and setting up its parameters
WidgetSliderPtr widget_slider = WidgetSlider::create(gui, 0, 360, 90);
widget_slider->setToolTip("This is my slider!");
widget_slider->arrange();
widget_slider->setPosition(100, 10);
gui->addChild(widget_label, Gui::ALIGN_OVERLAP | Gui::ALIGN_FIXED);
gui->addChild(widget_slider, Gui::ALIGN_OVERLAP | Gui::ALIGN_FIXED);
return 1;
}In order to use GUI elements we must specify handlers for various events (click, change, etc.). The following code demonstrates how to set event handlers:Чтобы использовать элементы графического интерфейса, мы должны указать обработчики для различных событий (щелчок, изменение и т.д.). Следующий код демонстрирует, как настроить обработчики событий:
#include <UnigineUserInterface.h>
// injecting Unigine namespace to the global namespace
using namespace Unigine;
GuiPtr gui;
/// function to be called when button1 is clicked
int onButton1Clicked()
{
/* .. */
}
/// method to be called when button2 is clicked
int AppWorldLogic::onButton2Clicked()
{
/* .. */
}
/// method to be called when delete button is clicked
int AppWorldLogic::onButtonDelClicked()
{
/* .. */
}
/// method to be called when slider position is changed
int AppWorldLogic::onSliderChanged()
{
/* .. */
}
int AppWorldLogic::init()
{
/* .. */
// getting a GUI pointer
gui = Gui::getCurrent();
// setting onButton1Clicked function as a clicked event handler for a buttonwidget1 using a CallbackBase variable
Unigine::CallbackBase* button1_clicked_callback_function = MakeCallback(onButton1Clicked);
buttonwidget1->addCallback(Gui::CLICKED, button1_clicked_callback_function);
// setting AppWorldLogic::onButton2Clicked method as a clicked event handler for a buttonwidget2 using a CallbackBase variable
Unigine::CallbackBase* button2_clicked_callback_method = MakeCallback(this, &AppWorldLogic::onButton2Clicked);
buttonwidget2->addCallback(Gui::CLICKED, button2_clicked_callback_method);
buttonwidget1->addCallback(Gui::CLICKED, MakeCallback(this, &AppWorldLogic::onButtonDelClicked));
// setting AppWorldLogic::onSliderChanged method as a changed event handler for a widget_slider
widget_slider->addCallback(Gui::CHANGED, MakeCallback(this, &AppWorldLogic::onSliderChanged));
/* .. */
return 1;
}Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on UI files, see the UI files article.Для получения дополнительной информации о файлах пользовательского интерфейса см. статью Файлы пользовательского интерфейса.
- For more information on GUI-related API, see the GUI-related classes section.Для получения дополнительной информации об API, связанном с графическим интерфейсом, см. раздел GUI-классы.
- For more information on the Gui class, see the Gui class article.Для получения дополнительной информации о классе Gui см. статью Gui class.
- For more information on handling events, see the Event Handling Callbacks article.Для получения дополнительной информации об обработке событий см. статью Обработка обратных вызовов событий.
Playing Sound and MusicВоспроизведение звука и музыки#
Источник звука SoundSource#
The SoundSource class is used to create directional sound sources. To create a sound source, create an instance of the SoundSource class and specify all required settings:Класс SoundSource используется для создания направленных источников звука. Чтобы создать источник звука, создайте экземпляр класса SoundSource и укажите все необходимые настройки:
// create a new sound source using the given sound sample file
SoundSourcePtr sound = SoundSource::create("sound.mp3");
// disable sound muffling when being occluded
sound->setOcclusion(0);
// set the distance at which the sound gets clear
sound->setMinDistance(10.0f);
// set the distance at which the sound becomes out of audible range
sound->setMaxDistance(100.0f);
// set the gain that result in attenuation of 6 dB
sound->setGain(0.5f);
// loop the sound
sound->setLoop(1);
// start playing the sound sample
sound->play();Источник AmbientSource#
To play ambient background music create an instance of the AmbientSource class, specify all required parameters and enable it. Make sure to import the sound asset to the project.Для воспроизведения фоновой музыки создайте экземпляр класса AmbientSource, укажите все необходимые параметры и включите его. Убедитесь, что вы импортировали звуковой ассет в проект.
// create a player so that an ambient sound source is played
PlayerSpectatorPtr player = PlayerSpectator::create();
player->setPosition(Vec3(0.0f, -3.401f, 1.5f));
player->setViewDirection(vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, -0.4f));
Game::setPlayer(player);
// create the ambient sound source
AmbientSourcePtr sound = AmbientSource::create("sound.mp3");
// set necessary sound settings
sound->setGain(0.5f);
sound->setPitch(1.0f);
sound->setLoop(1);
sound->play();Additional information: Дополнительная информация:
- For more information on directional sound, see the SoundSource class article.Для получения дополнительной информации о направленном звуке см. статью о классе SoundSource.
- For more information on ambient sound, see the AmbientSource class article.Для получения дополнительной информации об окружающем звуке см. статью о классе AmbientSource.
Setting Up PhysicsНастройка физики#
An object should have a body and a shape to be affected by gravity and to collide with other physical objects:Объект должен иметь тело и форму, чтобы на него воздействовала сила тяжести и он мог сталкиваться с другими физическими объектами:
// cube
MeshPtr meshBox = Mesh::create();
meshBox->addBoxSurface("box_surface", Math::vec3(1.0f));
ObjectMeshStaticPtr box = ObjectMeshStatic::create(meshBox);
// create a body and a shape based on the mesh
BodyRigidPtr bodyBox = BodyRigid::create(box);
ShapeBoxPtr shapeBox = ShapeBox::create(bodyBox, Math::vec3(1.0f));Catching Nodes with World TriggersОбнаружение объектов с помощью World Trigger#
A World trigger fires callbacks when any nodes (colliders or not) get inside or outside of them. The trigger can detect a node of any type by its bounding box. The trigger reacts to all nodes (default behavior).World trigger запускает обратные вызовы, когда какие-либо ноды (коллайдеры или нет) попадают внутрь или выходят из него. Триггер может обнаружить ноду любого типа по его ограничительной рамке. Триггер реагирует на все ноды (поведение по умолчанию).
The callback function of World Trigger is actually executed only when the next engine function is called: that is, before updatePhysics() (in the current frame) or before update() (in the next frame) — whatever comes first.Функция обратного вызова World Trigger фактически выполняется только тогда, когда вызывается следующая функция механизма: то есть перед updatePhysics() (в текущем кадре) или перед update() (в следующем кадре) — независимо от того, что будет первым.
The methods addEnterCallback() and addLeaveCallback() add callback functions to be fired when a node enters or leaves the World Trigger. A callback function must receive a Node as its first argument.Методы addEnterCallback() и addLeaveCallback() добавляют функции обратного вызова, которые запускаются, когда нода входит в World Trigger или выходит из него. Функция обратного вызова должна получать ноду в качестве своего первого аргумента.
// implement the enter callback
void AppWorldLogic::enter_callback(NodePtr node)
{
Log::message("\nA node named %s has entered the trigger\n", node->getName());
}
WorldTriggerPtr trigger;
int AppWorldLogic::init()
{
// create a world trigger node
trigger = WorldTrigger::create(Math::vec3(3.0f));
// add the enter callback to be fired when a node enters the world trigger
trigger->addEnterCallback(MakeCallback(this, &AppWorldLogic::enter_callback));
// add the leave callback to be fired when a node leaves the world trigger
trigger->addLeaveCallback(MakeCallback(this, &AppWorldLogic::leave_callback));
return 1;
}