Генерация физических объектов
We need some geometric primitives that the player can move around the Play Area and shoot at. Let's generate them via code.Нам нужны некоторые геометрические примитивы, по которым игрок может перемещаться по игровой площадке и стрелять. Давайте сгенерируем их с помощью кода.
A primitive should have a body and a shape to collide with the Player Character and be affected by gravity. We have implemented interaction with bullets via Intersections at the previous step, so we should set the BulletIntersection bit for the object's Intersection mask.Примитив должен иметь тело (body) и коллизионную форму (shape), чтобы сталкиваться с персонажем игрока и подвергаться воздействию гравитации. Мы реализовали взаимодействие с пулями через Пересечения на предыдущем шаге, поэтому мы должны установить бит BulletIntersection для маски Intersection объекта.
When the robot moves fast and the application framerate is low, the character will be teleported each frame and may go through physical objects due to discrete collision detection. To avoid this we are going to use continuous collision detection.Когда робот движется быстро, а частота кадров приложения низкая, персонаж будет телепортироваться каждый кадр и может проходить через физические объекты из-за дискретного обнаружения столкновений. Чтобы избежать этого, мы собираемся использовать непрерывное обнаружение столкновений.
-
Create a new C++ component in your IDE and call it ObjectGenerator. Copy the following code to the corresponding files and save the solution. This component generates the physical objects and places them in the world.Создайте новый компонент C++ в вашей IDE и назовите его ObjectGenerator. Скопируйте следующий код в соответствующие файлы и сохраните решение. Этот компонент генерирует физические объекты и размещает их в мире.
ObjectGenerator.h (C++)#include <UnigineComponentSystem.h> #include <UnigineGame.h> #pragma once class ObjectGenerator : public Unigine::ComponentBase { public: COMPONENT_DEFINE(ObjectGenerator, ComponentBase); COMPONENT_INIT(init, 1); // 1st initialization order protected: void init(); };ObjectGenerator.cpp (C++)#include "ObjectGenerator.h" using namespace Unigine; REGISTER_COMPONENT(ObjectGenerator); void ObjectGenerator::init() { // cube MeshPtr meshBox = Mesh::create(); meshBox->addBoxSurface("box_surface", Math::vec3(1.0f)); ObjectMeshStaticPtr box = ObjectMeshStatic::create(meshBox); box->setTriggerInteractionEnabled(1); box->setIntersectionMask(0x00000080, meshBox->findSurface("box_surface")); // check the BulletIntersection bit box->setWorldTransform(translate(Math::Vec3(0.5f, 7.5f, 1.0f))); box->setMaterialPath("materials/mesh_base_0.mat", "*"); box->setName("box"); Unigine::BodyRigidPtr bodyBox = BodyRigid::create(box); ShapeBoxPtr shapeBox = ShapeBox::create(bodyBox, Math::vec3(1.0f)); ShapeSphere::create(bodyBox, 0.5f); bodyBox->setShapeBased(0); bodyBox->setMass(2.0f); // sphere MeshPtr meshSphere = Mesh::create(); meshSphere->addSphereSurface("sphere_surface", 0.5f, 9, 32); ObjectMeshStaticPtr sphere = ObjectMeshStatic::create(meshSphere); sphere->setTriggerInteractionEnabled(1); sphere->setIntersectionMask(0x00000080, meshSphere->findSurface("sphere_surface")); // check the BulletIntersection bit sphere->setWorldTransform(translate(Math::Vec3(4.5f, 5.5f, 1.0f))); sphere->setMaterialPath("materials/mesh_base_1.mat", "*"); sphere->setName("sphere"); BodyRigidPtr bodySphere = BodyRigid::create(sphere); ShapeSphere::create(bodySphere, 0.5f); bodySphere->setShapeBased(0); bodySphere->setMass(2.0f); // capsule MeshPtr meshCapsule = Mesh::create(); meshCapsule->addCapsuleSurface("capsule_surface", 0.5f, 1.0f, 9, 32); ObjectMeshStaticPtr capsule = ObjectMeshStatic::create(meshCapsule); capsule->setTriggerInteractionEnabled(1); capsule->setIntersectionMask(0x00000080, meshCapsule->findSurface("capsule_surface")); // check the BulletIntersection bit capsule->setWorldTransform(translate(Math::Vec3(4.5f, 0.5f, 3.0f))); capsule->setMaterialPath("materials/mesh_base_2.mat", "*"); capsule->setName("capsule"); BodyRigidPtr bodyCapsule = BodyRigid::create(capsule); ShapeCapsule::create(bodyCapsule, 0.5f, 1.0f); bodyCapsule->setShapeBased(0); bodyCapsule->setMass(2.0f); }ПримечаниеDo not change the size of an object after the creation. The physics doesn't support scaling nodes with Body attached. Не изменяйте размер объекта после создания. Физика не поддерживает масштабирование нод с прикрепленным Body. - Build and run the solution in your IDE to generate a property file for the component.Создайте и запустите решение в вашей среде разработки, чтобы сгенерировать файл свойств для компонента.
- Switch back to the UnigineEditor and create a new Dummy Node, rename it to "object_generator", and place it somewhere in the world.Переключитесь обратно на UnigineEditor и создайте новую Dummy Node, переименуйте ее в "object_generator" и поместите его где-нибудь в мире.
- Attach the created ObjectGenerator component to the "object_generator" node to make it generate physical objects on the initialization.Присоедините созданный компонент ObjectGenerator к ноде "object_generator", чтобы она генерировала физические объекты при инициализации.
-
Create 3 new materials in the UnigineEditor: in the Materials window, right-click the mesh_base material and choose Create Child. By default, the created materials are named as specified in the previous code snippet (mesh_base_*). Move the materials to the data/materials folder of your project (create this folder if it doesn't exist).Создайте 3 новых материала в UnigineEditor: в окне Materials щелкните правой кнопкой мыши материал mesh_base и выберите Create Child. По умолчанию созданные материалы называются так, как указано в предыдущем фрагменте кода (mesh_base_*). Переместите материалы в папку data/materials вашего проекта (создайте эту папку, если ее не существует).
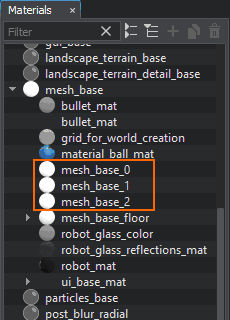
-
Select materials one by one in the Materials window and in the Parameters window switch to the Parameters tab and click on the color field near Albedo to choose different colors for the objects via the color picker.Выберите материалы один за другим в окне Materials, а в окне Parameters переключитесь на вкладку Parameters и нажмите на цветовое поле рядом с Albedo, чтобы выбрать разные цвета для объектов.

- Save changes to the world via Ctrl + S.Сохраните изменения в мире с помощью Ctrl + S.
- Run the project in your IDE to see the spawned physical objects in the world.Запустите проект в своей среде разработки, чтобы увидеть созданные физические объекты в мире.
