Handling Contacts on Collision
Sometimes you may need to implement your own contact handler for colliding physical bodies. In this example, you will learn how to visualize contact points, display debug information, and add a hit effect (sparks) at the point of impact.
Preparing the content#
To create sparks, we are going to use the VFX add-on (you can download it on https://store.unigine.com).
Create a new project in UNIGINE SDK Browser and import the VFX add-on to it.
When you open the project in the UnigineEditor, you will see the default scene containing some dynamic objects. Let's create another box and get some information about the contacts it will have with other objects.

Making the Objects Collidable#
The box is a dynamic object, so to be able to collide it needs a body and a collision shape. Add a Rigid body and a shape via the Physics tab of the Parameters window.
Collisions are available for static objects as well (like buildings or ground) — simply enable the Collision option for the corresponding surface.
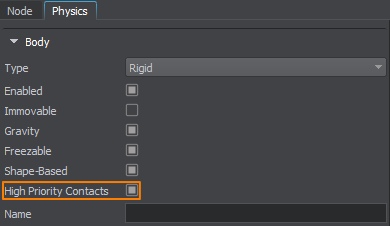
Enabling High Priority Contacts#
On collision, contacts are distributed randomly between the interacting bodies to optimize performance: some are handled by the first body, others by the second. For a body, contacts that it handles itself are internal (access to them is fast), and contacts handled by other bodies are external.
The box is a high-priority body for us and we want to track its collisions with maximum efficiency. We can make the box handle most of its contacts itself (so that most of them are internal). To do so, select the box and check High Priority Contacts in the Physics tab (or do it via code).
Creating a Hit Effect Node#
We will use a Particle System to create a node that simulates sparks.
-
In the UnigineEditor, click Create -> Particle System -> Particles. Place the object somewhere in the world, rename it to sparks, and adjust its parameters:
- Number Per Spawn = 10
- Radius = 0.02
- Life Time = 0.2
- Period = inf
- Duration = 0
- In the Surface Material section, assign library_spark1.mat material (it is located in the data -> vfx -> materials -> library_vfx folder of your project).
- Switch to the data folder in the Asset Browser. Right-click the sparks node and select Create a Node Reference. A sparks.node file will be generated in the data folder.
- Delete the sparks object from the scene, we no longer need it since it will be loaded via code.
Algorithm Description#
The algorithm we are going to use can be described as follows:
- We create three variables (lastContactTime, lastContactPoint, lastContactInfo) to keep the time and position of the last occurred contact and some info about it.
- We subscribe for an event to perform some actions when each contact emerges. The handler function (OnContactEnter()) takes the body and the index of the contact.
- If the contact is internal, we save its time and position.
-
We get both physical bodies participating in this contact (body0, body1). We check if our box has hit another physical object.
- If any of body0 and body1 exists (and it is not the body of our box), then we have found this object. We get details about this body and render it in the viewport using Visualizer.
- Otherwise, the box has hit some static object (a surface with the Collision option enabled). We make this surface highlighted in the viewport as well.
- We add details we are interested in (e.g., the contact impulse).
- We spawn a hit effect if the impulse is strong enough. Physics event handlers are called in the main thread, so it is safe to create nodes inside the OnContactEnter() function.
- Finally, in the Update() method we display the info and create a slow motion effect for one second.
Component Code#
Create a new C# component, call it ContactsHandler, and open it in your IDE.
[Component(PropertyGuid = "YOUR_COMPONENT_GUID")]Copy the source code below and save it to the ContactsHandler.cs file.
ContactsHandler.cs
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Unigine;
#region Math Variables
#if UNIGINE_DOUBLE
using Vec3 = Unigine.dvec3;
#else
using Vec3 = Unigine.vec3;
#endif
#endregion
// DO NOT CHANGE THE PropertyGuid VALUE
[Component (PropertyGuid = "YOUR_GUID")]
public class ContactsHandler : Component
{
// For debugging
public bool debug = true;
// A node that will be loaded on contact (a hit effect in our case)
public AssetLinkNode contactEffect;
// Time, position and some info of the last occurred contact
private DateTime lastContactTime;
private Vec3 lastContactPoint;
private string lastContactInfo;
private void Init()
{
Body body = node.ObjectBody;
if (body)
{
// For debug purposes, we can render certain contacts depending on their type
body.EventContacts.Connect((b) => b.RenderInternalContacts());
// A handler to be fired when each contact emerges
body.EventContactEnter.Connect(OnContactEnter);
}
}
// This function takes the body and the index of the contact
private void OnContactEnter(Body body, int num)
{
// Enable Visualizer to see the rendered contact points
Visualizer.Enabled = true;
if(body.IsContactInternal(num))
{
if (debug)
{
// The time of the contact
lastContactTime = DateTime.Now;
// The position of the contact
lastContactPoint = body.GetContactPoint(num);
// We get both physical bodies participating in this contact
Body body0 = body.GetContactBody0(num);
Body body1 = body.GetContactBody1(num);
Body touchedBody = null;
// We check if our object has hit another physical object.
// If any of the bodies exists and it's not the body of our object
// then we have found another physics-driven object that hit it
if (body0 && body0 != body) touchedBody = body0;
if (body1 && body1 != body) touchedBody = body1;
if (touchedBody)
{
// Our object has touched a physics-driven object.
// We save the info about the body
lastContactInfo = $"body {touchedBody.Name} of {touchedBody.Object.Name}";
// Render it in the viewport
Visualizer.RenderObject(touchedBody.Object, vec4.BLUE, 0.5f);
}
else
{
// It has touched a surface with Collision enabled
lastContactInfo = $"surface #{body.GetContactSurface(num)} of {body.GetContactObject(num).Name}";
// Highlighting the surface
Visualizer.RenderObjectSurface(body.GetContactObject(num), body.GetContactSurface(num), vec4.BLUE, 0.5f);
}
// You can add details you are interested in (e.g., the contact impulse)
lastContactInfo += $"\nimpulse: {body.GetContactImpulse(num):0.0}";
}
// We spawn a hit effect if the impulse is strong enough
if (body.GetContactImpulse(num) > 0.3f && !contactEffect.IsNull)
{
contactEffect.Load(body.GetContactPoint(num), MathLib.RotationFromDir(body.GetContactNormal(num) * MathLib.RotateY(90)));
}
}
}
private void Update()
{
// Here we display the info and create a slow motion effect for one second
if (debug)
{
if((DateTime.Now - lastContactTime).Seconds < 1.0f)
{
// Slow motion effect
Game.Scale = 0.4f;
Visualizer.RenderMessage3D(lastContactPoint, vec3.ONE, $"last contact: \n{lastContactInfo}", vec4.GREEN, 2, 24);
}
else
{
// All the other time the speed will be normal
Game.Scale = 1.0f;
}
}
}
}Applying Logic to the Object#
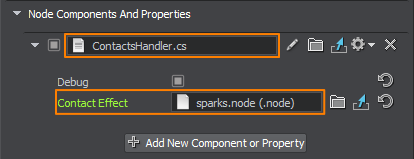
Switch to the UnigineEditor and assign the ContactsHandler component to the box node.
Specify the sparks.node in the Contact Effect field.
Adjust the position/rotation of the first_person_controller node to get a better initial view of the scene.
Click Run to see the result. As the box is rolling around, the physics-driven objects and collidable surfaces it hits along the way are highlighted, and contact details are displayed near the contact point. Whenever a collision occurs, it triggers an asset spawning and a slow motion effect.
To disable the debug information, uncheck the Debug box under Node Components And Properties.
This is how you can easily track collisions and run necessary logic on time: spawn particles, play sounds, and destroy fracture objects.
The information on this page is valid for UNIGINE 2.20 SDK.