Unigine.ObjectParticles Class
| Inherits from: | Object |
This class is used to create particle systems. The particles are approximated with a sphere. They can be of different types (see the details) and radius (that can change with time). They are emitted from different emitters (see the details) with a specified spawn rate. The particles disappear after the set life time period or culled when hitting other nodes. They either collide with the outer surface of the approximation sphere or intersect only by the its center.
The particle flow direction can be influenced by:
- Gravity
- Point force (see the details), which has two properties:
- Deflectors of two types (see the details):
- Physicals nodes
The particle system can also initialized before it actually appears, so that it starts to be rendered with already spawned particles.
Usage Example#
Particles parameters are set via Particle Modifiers. Based on the modifier's type, a parameter could be a scalar(0.8f) or a vector (vec4.BLUE). It can be:
- a constant value
- a random value varying between a minimum and maximum limits
- a value defined by a curve
- a random value between the upper and lower limits defined by the two curves at each point of the lifetime
See here for more information on different modes for modifiers.
[Component(PropertyGuid = "AUTOGENERATED_GUID")] // <-- this line is generated automatically for a new component
public class ParticleSystemCreator : Component
{
ObjectParticles particles;
Curve2d curve;
private void Init()
{
particles = new ObjectParticles();
particles.WorldTransform = new Mat4(new quat(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
particles.GetMaterialInherit(0).SetParameterFloat4("albedo_color", vec4.GREEN);
// enable the emitter and specify its settings
particles.EmitterEnabled = true;
particles.SpawnRate = 2000.0f;
particles.SetLife(5.0f, 0.5f);
// create a new 2d curve object
curve = new Curve2d();
curve.AddKey(new vec2(0.0f, 0.15f));
curve.AddKey(new vec2(0.5f, 0.25f));
curve.AddKey(new vec2(1.0f, 0.5f));
curve.AddKey(new vec2(1.5f, 0.35f));
// change the modifier's mode to the curve mode
particles.RadiusOverTimeModifier.Mode = ParticleModifier.MODE.CURVE;
// set the curve to define the modifier
particles.RadiusOverTimeModifier.Curve = curve;
// set parameters using scalar values
particles.GrowthOverTimeModifier.ConstantMin = 0.0f;
particles.GrowthOverTimeModifier.ConstantMax = 0.2f;
particles.VelocityOverTimeModifier.Constant = 0.3f;
// set the parameter using a vector value
particles.GravityOverTimeModifier.Constant = new vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 4.0f);
}
private void Update()
{
float time = Game.Time;
particles.WorldTransform = new Mat4(MathLib.RotateZ(time * 64.0f) * MathLib.Translate(15.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
}
private void Shutdown()
{
particles.DeleteLater();
}
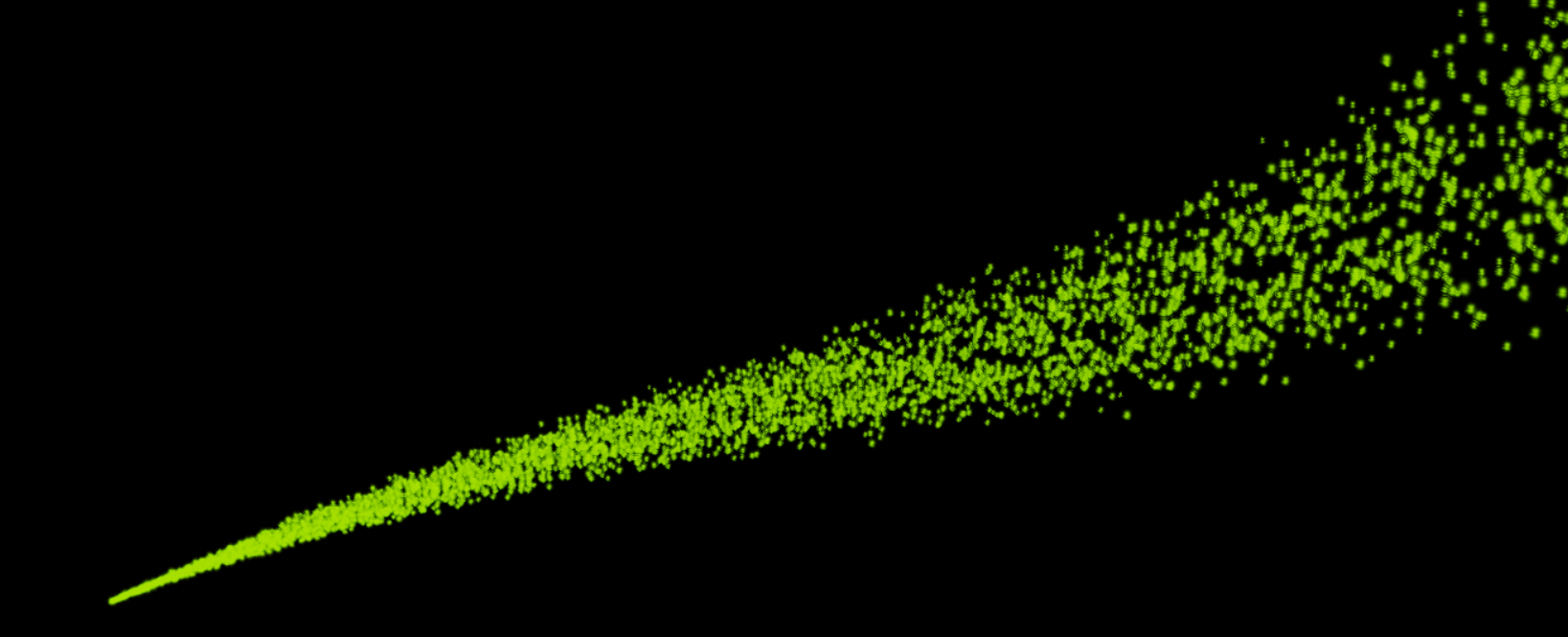
}If you launch the application, you get the following particle system:
Synchronizing Particles#
For image consistency in multi-channel rendering use cases, Particle Systems can have more deterministic behavior, i.e. when a particle is spawned on one PC, it can travel to another screen seamlessly.
To synchronize the particle systems across several applications, it is required to define which application is the Master one — it will count all particles and provide all related info via the network to Slaves — applications that only receive data and reproduce them.
[Component(PropertyGuid = "AUTOGENERATED_GUID")] // <-- this line is generated automatically for a new component
public class ParticleSystemSync : Component
{
public ObjectParticles particles; // particles that are going to be synchronized
bool is_master = true; // or false, if the application is a Slave
Socket socket; // example of a socket used to send the particles data
private void Init()
{
// create and open a stream
socket = new Socket(0);
socket.Open("127.255.255.255", 8889);
// For every type of the application, define the particles operation mode
if (is_master)
particles.SyncMode = ObjectParticles.SYNC_MODE.MASTER;
else
particles.SyncMode = ObjectParticles.SYNC_MODE.SLAVE;
}
private void Update()
{
if (is_master)
{
Blob data = new Blob();
particles.TakeSyncData(data);
socket.Write(data.GetData(), data.GetSize());
}
else
{
Blob data = new Blob();
socket.ReadStream(data, 1048576); // 1Mb, maximum size of the packet
data.SeekSet(0); // Moving the pointer to the first symbol,
// because after reading the data from the socket,
// the pointer is at the end of the data.
particles.ApplySyncData(data);
}
}
private void Shutdown()
{
// closing the socket
socket.Close();
// destroying the socket
socket.DeleteLater();
}
}ObjectParticles Class
Enums
SYNC_MODE#
Synchronization mode to be used for the particle system.Properties
WorldBoundBox WorldBoundBoxParticles#
BoundBox BoundBoxSimulation#
BoundBox BoundBoxParticles#
vec3 WorldOffset#
int NumContacts#
int NumDeflectors#
int NumNoises#
int NumForces#
vec3 EmitterVelocity#
vec3 EmitterSize#
int EmitterSync#
int EmitterSequence#
bool EmitterContinuous#
bool EmitterShift#
bool EmitterBased#
bool EmitterEnabled#
int ProceduralParenting#
int ProceduralPositioning#
bool ProceduralRendering#
int EmitterType#
float Roughness#
float Restitution#
float LinearDamping#
float PhysicalMass#
int PhysicalMask#
int NumParticles#
float SpawnThreshold#
float SpawnScale#
float SpawnRate#
ivec2 TextureAtlasSize#
int NumberPerSpawn#
bool ClearOnEnable#
int Culling#
int Collision#
int PhysicsIntersection#
int TextureAtlas#
int VariationY#
int VariationX#
int DepthSort#
float MaxWarmingTime#
int Warming#
int ParticlesType#
uint Seed#
ObjectParticles.SYNC_MODE SyncMode#
float UpdateDistanceLimit#
int FPSInvisible#
int FPSVisibleShadow#
int FPSVisibleCamera#
ParticleModifierVector PositionOverTimeModifier#
ParticleModifierVector DirectionOverTimeModifier#
ParticleModifierScalar VelocityOverTimeModifier#
ParticleModifierScalar LengthFlatteningOverTimeModifier#
ParticleModifierScalar LengthStretchOverTimeModifier#
ParticleModifierScalar GrowthOverTimeModifier#
ParticleModifierScalar RadiusOverTimeModifier#
ParticleModifierScalar RotationOverTimeModifier#
ParticleModifierScalar AngleOverTimeModifier#
int EmitterLimitPerSpawn#
ParticleModifierVector GravityOverTimeModifier#
Members
ObjectParticles ( ) #
Constructor. Creates a particle system.vec3 GetContactNormal ( int num ) #
Returns the point of the particles collision with other objects.Arguments
- int num - The collision point number.
Return value
Collision point coordinates.Object GetContactObject ( int num ) #
Returns the object that collided with particles collided in a given collision point.Arguments
- int num - The collision point number.
Return value
The object participated in collision.vec3 GetContactPoint ( int num ) #
Returns the normal vector for the collision point of the particles with other objects.Arguments
- int num - The collision point number.
Return value
Normal vector coordinates.vec3 GetContactVelocity ( int num ) #
Returns the velocity in the collision point of the particles with other objects.Arguments
- int num - The collision point number.
Return value
Velocity values for each of space dimensions.void SetDeflectorAttached ( int num, int attached ) #
Attaches or detaches a given deflector to the particle system.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
- int attached - 1 to attach the deflector, 0 to detach it.
int IsDeflectorAttached ( int num ) #
Returns a value indicating if a given deflector is attached to the particle system.Arguments
- int num - Number of the deflector.
Return value
1 if the deflector is attached; otherwise, 0.void SetDeflectorEnabled ( int num, bool enabled ) #
Enables or disables the given deflector.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
- bool enabled - true to enable the deflector, false to disable it.
bool IsDeflectorEnabled ( int num ) #
Returns a value indicating if the given deflector is enabled.Arguments
- int num - Number of the deflector.
Return value
true if the deflector is enabled; otherwise, false.void SetDeflectorRestitution ( int num, float restitution ) #
Sets restitution of the deflector. Makes sense only for reflectors.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
- float restitution - A new restitution. The provided value will be saturated in the range [0; 1].
float GetDeflectorRestitution ( int num ) #
Returns the current restitution of the deflector. Makes sense only for reflectors.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
Return value
The current restitution.void SetDeflectorRoughness ( int num, float roughness ) #
Sets roughness of the deflector surface. Makes sense only for reflectors.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
- float roughness - A new roughness. The provided value will be saturated in the range [0; 1].
float GetDeflectorRoughness ( int num ) #
Returns the current roughness of the deflector. Makes sense only for reflectors.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
Return value
The current roughness.void SetDeflectorSize ( int num, vec3 size ) #
Sets dimensions of a given deflector.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
- vec3 size - New dimensions. Only the first two components are taken into account (x and y).
vec3 GetDeflectorSize ( int num ) #
Returns the current dimensions of the given deflector.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
Return value
The current dimensions. Only the first two components should be taken into account (x and y).void SetDeflectorTransform ( int num, mat4 transform ) #
Sets a transformation matrix for a given deflector. This matrix describes the position and orientation of the deflector.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
- mat4 transform - A new transformation matrix.
mat4 GetDeflectorTransform ( int num ) #
Returns the transformation matrix of a given deflector. This matrix describes the position and orientation of the deflector. The default is the identity matrix.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
Return value
The transformation matrix.void SetDeflectorType ( int num, int type ) #
Sets a type of a given deflector.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
- int type - OBJECT_PARTICLES_DEFLECTOR_REFLECTOR or OBJECT_PARTICLES_DEFLECTOR_CLIPPER.
int GetDeflectorType ( int num ) #
Returns a type of a given deflector.Arguments
- int num - The deflector number.
Return value
DEFLECTOR_REFLECTOR or DEFLECTOR_CLIPPER.void SetDelay ( float mean, float spread ) #
Sets delay of particle system initialization relative to the parent particle one.Arguments
- float mean - A mean value in seconds. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead.
- float spread - A spread value in seconds.
float GetDelayMean ( ) #
Returns the mean value of particles initialization delay relative to the parent particle system.Return value
The mean value in seconds.float GetDelaySpread ( ) #
Returns the spread value of particles initialization delay relative to the parent particle system.Return value
The spread value in seconds.void SetDuration ( float mean, float spread ) #
Sets a duration of each particle emission in seconds.Arguments
- float mean - Mean value in seconds. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead.
- float spread - Spread value in seconds.
float GetDurationMean ( ) #
Returns the current mean value of particle emission intervals.Return value
The mean value in seconds.float GetDurationSpread ( ) #
Returns the current spread value of particle emission intervals.Return value
The spread value in seconds.void SetForceAttached ( int num, int attached ) #
Attaches or detaches the given force to the particle system.Arguments
- int num - Force number in the range from 0 to the total number of forces.
- int attached - 1 to attach the force, 0 to detach it.
int IsForceAttached ( int num ) #
Returns a value indicating if the given force is attached to the particle system.Arguments
- int num - Force number in the range from 0 to the total number of forces.
Return value
1 if the force is attached; otherwise, 0.void SetForceAttenuation ( int num, float attenuation ) #
Sets an attenuation factor for the specified force.Arguments
- int num - Force number in the range from 0 to the total number of forces.
- float attenuation - An attenuation factor.
float GetForceAttenuation ( int num ) #
Returns the current attenuation factor for the specified force.Arguments
- int num - Force number in the range from 0 to the total number of forces.
Return value
The current attenuation factor.void SetForceAttractor ( int num, float attractor ) #
Sets the attraction force that will be applied to the particles in the specified force radius.Arguments
- int num - The attraction force number.
- float attractor - The force value.
float GetForceAttractor ( int num ) #
Returns the current attraction force applied to the particles in the specified force radius.Arguments
- int num - The attraction force number.
Return value
The force value.void SetForceEnabled ( int num, bool enabled ) #
Enables or disables the given force.Arguments
- int num - The force number.
- bool enabled - 1 to enable the force, 0 to disable it.
bool IsForceEnabled ( int num ) #
Returns a value indicating if the given force is enabled.Arguments
- int num - Number of the force.
Return value
1 if the force is enabled; otherwise, 0.void SetForceRadius ( int num, float radius ) #
Sets a radius for applying the force.Arguments
- int num - The force number.
- float radius - A radius in units. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead.
float GetForceRadius ( int num ) #
Returns the current radius set for applying the force.Arguments
- int num - The force number.
Return value
The current radius in units.void SetForceRotator ( int num, float rotator ) #
Sets a rotation force that will be applied to the particles in the specified force radius.Arguments
- int num - The rotation force number.
- float rotator - The force value.
float GetForceRotator ( int num ) #
Returns the current rotation force applied to the particles in the specified force radius.Arguments
- int num - The rotation force number.
Return value
The force value.void SetForceTransform ( int num, mat4 transform ) #
Sets a transformation matrix for the specified force.Arguments
- int num - The force number.
- mat4 transform - A transformation matrix.
mat4 GetForceTransform ( int num ) #
Returns the current transformation matrix for the specified force.Arguments
- int num - The force number.
Return value
The transformation matrix.void SetLife ( float mean, float spread ) #
Sets a lifetime duration of particles in seconds.Arguments
- float mean - A mean value in seconds. If a too small value is provided, 1E-6 will be used instead.
- float spread - A spread value in seconds.
float GetLifeMean ( ) #
Returns the current mean value of particle lifetime duration.Return value
The mean value in seconds.float GetLifeSpread ( ) #
Returns the current spread value of particle lifetime duration.Return value
The spread value in seconds.void SetNoiseAttached ( int num, int attached ) #
Sets the noise as an attached.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
- int attached - 1 to enable the Attached flag, 0 to disable it.
int IsNoiseAttached ( int num ) #
Returns a value indicating if the given noise is attached to the particle system.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
1 if the noise is attached; otherwise, 0.void SetNoiseEnabled ( int num, bool enabled ) #
Enables or disables the given noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
- bool enabled - 1 to enable the noise, 0 to disable it.
bool IsNoiseEnabled ( int num ) #
Returns a value indicating if the given noise is enabled.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
1 if the noise is enabled; otherwise, 0.void SetNoiseForce ( int num, float force ) #
Sets the Force parameter value for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
- float force - The noise force value.
float GetNoiseForce ( int num ) #
Returns the Force parameter value for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
The noise force value.void SetNoiseFrequency ( int num, int frequency ) #
Sets the Frequency parameter value for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
- int frequency - The noise frequency value.
int GetNoiseFrequency ( int num ) #
Returns the Frequency parameter value for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
The noise frequency value.Image GetNoiseImage ( int num ) #
Returns the spatial texture for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
The texture of the noise.void SetNoiseOffset ( int num, vec3 offset ) #
Sets the Offset parameter coordinates values for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
- vec3 offset - Offset coordinates values.
vec3 GetNoiseOffset ( int num ) #
Returns the Offset parameter coordinates values for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
Offset coordinates values.void SetNoiseScale ( int num, float scale ) #
Sets the Scale parameter value for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
- float scale - The noise scale value.
float GetNoiseScale ( int num ) #
Returns the Scale parameter value for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
The noise scale value.void SetNoiseSize ( int num, int size ) #
Sets the Size parameter value for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
- int size - Noise size value.
int GetNoiseSize ( int num ) #
Returns the Size parameter value for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
The noise size value.void SetNoiseStep ( int num, vec3 step ) #
Sets the Step parameter coordinates values for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
- vec3 step - Step coordinates values.
vec3 GetNoiseStep ( int num ) #
Returns the Step parameter coordinates values for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
Step coordinates values.void SetNoiseTransform ( int num, mat4 transform ) #
Sets the transformation matrix for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
- mat4 transform - The noise transformation matrix.
mat4 GetNoiseTransform ( int num ) #
Returns the transformation matrix for the required noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
The noise transformation matrix.vec3 GetParticlePosition ( int num ) #
Returns the position of a given particle.Arguments
- int num - The particle number.
Return value
Position coordinates for the particle.float GetParticleRadius ( int num ) #
Returns the radius of a given particle.Arguments
- int num - The particle number.
Return value
Radius of the particle.void GetParticleTransforms ( mat4[] transforms ) #
Returns transformation matrices for spawned particles.Arguments
- mat4[] transforms - Array to which the transformation matrices will be added.
vec3 GetParticleVelocity ( int num ) #
Returns the velocity vector for a specified particle.Arguments
- int num - The particle number.
Return value
The velocity vector.void SetPeriod ( float mean, float spread ) #
Sets an interval of emitter inactivity in seconds.Arguments
- float mean - A mean value in seconds. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead.
- float spread - A spread value in seconds.
float GetPeriodMean ( ) #
Returns the current mean value of emitter inactivity intervals.Return value
The mean value in seconds.float GetPeriodSpread ( ) #
Returns the current spread value of emitter inactivity intervals.Return value
The spread value in seconds.void SetProceduralTextureResolution ( vec3 res ) #
Sets the resolution of the procedural texture.Arguments
- vec3 res - Resolution of the texture.
vec3 GetProceduralTextureResolution ( ) #
Returns the resolution of the procedural texture.Return value
Resolution of the texture.int AddDeflector ( ) #
Adds a deflector with default settings.Return value
The number of the new deflector in the list of deflectors.void AddEmitterSpark ( vec3 point, vec3 normal, vec3 velocity ) #
Adds a spark emitter in the given point.Arguments
- vec3 point - Point for sparks emission.
- vec3 normal - Normal of the point of spark emission.
- vec3 velocity - Velocity in the point of spark emission (velocity of source particles or node by contact).
int AddForce ( ) #
Adds a force with default settings.Return value
The number of the new force in the list of forces.int AddNoise ( ) #
Adds a new noise with default settings.Return value
The number of the new noise in the list of noises.void ClearParticles ( ) #
Deletes all particles spawned by the emitter.void RemoveDeflector ( int num ) #
Removes a given point deflector.Arguments
- int num - Number of the deflector to remove.
void RemoveForce ( int num ) #
Removes the given force.Arguments
- int num - The number of the force to remove.
void RemoveNoise ( int num ) #
Removes the given noise.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
static int type ( ) #
Returns the type of the object.Return value
Object Particles type identifier.bool SaveStateSelf ( Stream stream ) #
Saves the object's state to the stream.Saving into the stream requires creating a blob to save into. To restore the saved state the RestoreStateSelf() method is used:
// initialize a object and set its state
//...//
// save state
Blob blob_state = new Blob();
object.SaveStateSelf(blob_state);
// change the state
//...//
// restore state
blob_state.SeekSet(0); // returning the carriage to the start of the blob
object.RestoreStateSelf(blob_state);Arguments
- Stream stream - Stream instance.
Return value
true on success; otherwise, false.bool RestoreStateSelf ( Stream stream ) #
Restores the object's state from the stream.Restoring from the stream requires creating a blob to save into and saving the state using the saveStateSelf() method:
// initialize a object and set its state
//...//
// save state
Blob blob_state = new Blob();
object.SaveStateSelf(blob_state);
// change the state
//...//
// restore state
blob_state.SeekSet(0); // returning the carriage to the start of the blob
object.RestoreStateSelf(blob_state);Arguments
- Stream stream - Stream instance.
Return value
true on success; otherwise, false.int SaveStateForces ( Stream stream ) #
Saves the state of the object's forces to the specified stream.Saving into the stream requires creating a blob to save into. To restore the saved state the RestoreStateForces() method is used:
// initialize a object and set its state
//...//
// save state
Blob blob_state = new Blob();
object.SaveStateForces(blob_state);
// change the state
//...//
// restore state
blob_state.SeekSet(0); // returning the carriage to the start of the blob
object.RestoreStateForces(blob_state);Arguments
- Stream stream - Stream instance.
bool RestoreStateForces ( Stream stream ) #
Restores the state of the object's forces from the specified stream.Restoring from the stream requires creating a blob to save into and saving the state using the saveStateForces() method:
// initialize a object and set its state
//...//
// save state
Blob blob_state = new Blob();
object.SaveStateForces(blob_state);
// change the state
//...//
// restore state
blob_state.SeekSet(0); // returning the carriage to the start of the blob
object.RestoreStateForces(blob_state);Arguments
- Stream stream - Stream instance.
Return value
true on success; otherwise, false.bool SaveStateNoises ( Stream stream ) #
Saves the state of the object's noises to the specified stream.Saving into the stream requires creating a blob to save into. To restore the saved state the RestoreStateNoises() method is used:
// initialize a object and set its state
//...//
// save state
Blob blob_state = new Blob();
object.SaveStateNoises(blob_state);
// change the state
//...//
// restore state
blob_state.SeekSet(0); // returning the carriage to the start of the blob
object.RestoreStateNoises(blob_state);Arguments
- Stream stream - Stream instance.
Return value
true on success; otherwise, false.bool RestoreStateNoises ( Stream stream ) #
Restores the state of the object's noises from the specified stream.Restoring from the stream requires creating a blob to save into and saving the state using the saveStateNoises() method:
// initialize a object and set its state
//...//
// save state
Blob blob_state = new Blob();
object.SaveStateNoises(blob_state);
// change the state
//...//
// restore state
blob_state.SeekSet(0); // returning the carriage to the start of the blob
object.RestoreStateNoises(blob_state);Arguments
- Stream stream - Stream instance.
Return value
true on success; otherwise, false.bool SaveStateDeflectors ( Stream stream ) #
Saves the state of the object's deflectors to the specified stream.Saving into the stream requires creating a blob to save into. To restore the saved state the RestoreStateDeflectors() method is used:
// initialize a object and set its state
//...//
// save state
Blob blob_state = new Blob();
object.SaveStateDeflectors(blob_state);
// change the state
//...//
// restore state
blob_state.SeekSet(0); // returning the carriage to the start of the blob
object.RestoreStateDeflectors(blob_state);Arguments
- Stream stream - Stream instance.
Return value
true on success; otherwise, false.bool RestoreStateDeflectors ( Stream stream ) #
Restores the state of the object's deflectors from the specified stream.Restoring from the stream requires creating a blob to save into and saving the state using the saveStateDeflectors() method:
// initialize a object and set its state
//...//
// save state
Blob blob_state = new Blob();
object.SaveStateDeflectors(blob_state);
// change the state
//...//
// restore state
blob_state.SeekSet(0); // returning the carriage to the start of the blob
object.RestoreStateDeflectors(blob_state);Arguments
- Stream stream - Stream instance.
Return value
true on success; otherwise, false.void SetNoiseSeed ( int num, int seed ) #
Sets a new random seed value to be used for the noise with the specified number. This parameter is used to synchronize pseudorandom number generators for particle system noises.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
- int seed - Random seed value to be used for the target noise.
int GetNoiseSeed ( int num ) #
Returns the random seed value currently used for the noise with the specified number. This parameter is used to synchronize pseudorandom number generators for particle system noises.Arguments
- int num - Target noise number.
Return value
Random seed value currently used for the target noise.void TakeSyncData ( Stream stream ) #
Writes particle synchronization data to the specified stream. This method should be used by the particle system with the master sync mode.Arguments
- Stream stream - Stream to which particle synchronization data is to be written.
void ApplySyncData ( Stream stream ) #
Reads particle synchronization data from the specified stream and applies it to the particle system. This method should be used by the particle system with the slave sync mode.Arguments
- Stream stream - Stream with particle synchronization data to be applied.
void SetTextureAtlasSize ( ivec2 size ) #
Sets the NxN size of the texture atlas for the particles.Arguments
- ivec2 size - The size of the texture atlas to be used.