Sample Texture Node
Description
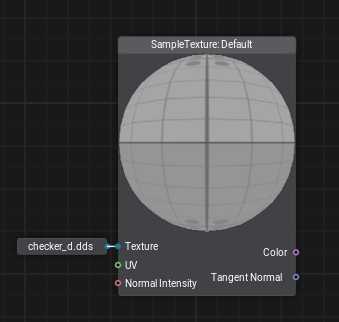
Takes an input texture (2D, 3D, 2D array, 2D int, or cubemap) and returns a value from this texture depending on the current parameter values selected for this node, other inputs are used to provide additional information required to obtain output.
This node automatically detects the type of texture connected to its input (2D, 3D, 2D array, 2D int, or cubemap) and what it is going to be used for. For example, if you connect a 2D Texture the node will automatically activate a UV input, for a 2D Texture Array it will expect UV and array element Index, for a 3D Texture - UVW coordinates, or a Direction vector for cubemaps (Texture Cube), for Texture 2D Int nodes an integer output is activated. Moreover, this node contains settings for interpolation of values when sampling a texture (filtering).
Parameters
Type |
|---|
Sampling and filtering type to be used. One of the following options::
|
Normal Space |
|---|
Normal space to be used. One of the following options::
|
The information on this page is valid for UNIGINE 2.19 SDK.