Using Manipulators to Transform Objects
After adding an object to the scene in Unigine Editor, you can control object transformations with control devices. But sometimes transformations are supposed to be made at application runtime. For example, when you create your own game with a world editor, where you can place objects in the world and move them around.
This usage example will teach you how to:
- Select an object on the screen with the mouse using Intersections.
- Use manipulator widgets to modify the object transform matrix.
- Switch between different manipulator widgets using the keyboard.
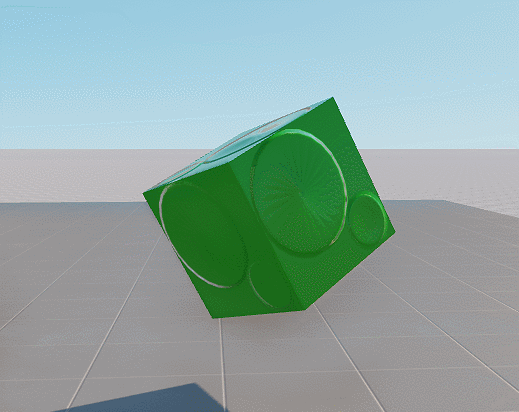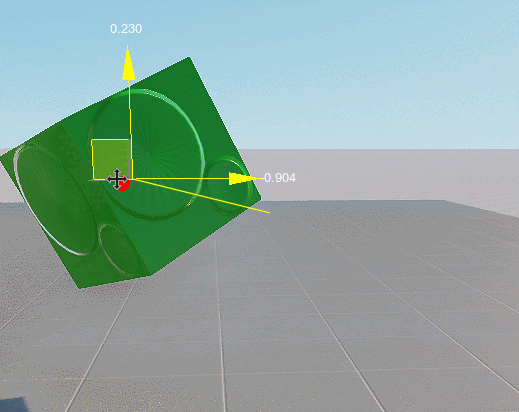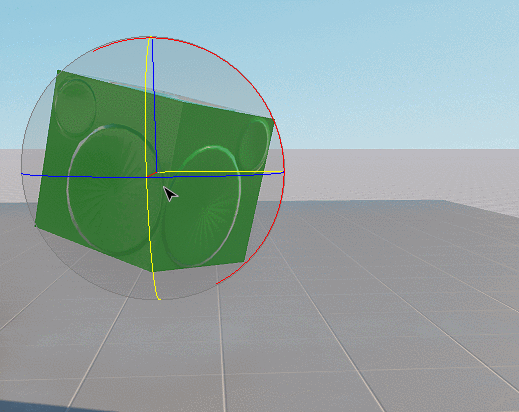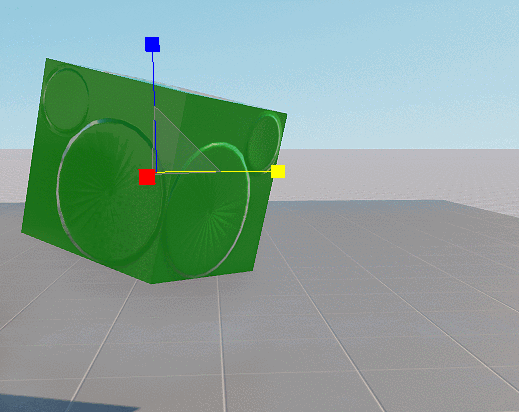
See Also#
- An article on Matrix Transformations.
- An article on Intersections.
Creating Manipulators to Control Object Transformations#
There are 3 types of manipulator widgets used for object transforming:
- Widget Manipulator Translator creates a mover manipulator used to translate objects along three axes with arrows at the end.
- Widget Manipulator Rotator creates a rotation manipulator used to rotate objects around three axes in the form of a sphere.
- Widget Manipulator Scaler creates a scaling manipulator used to scale objects along three axes in the form of a triangle.
All these manipulators work the same way, each of them visually represents a part of the transformation matrix that you can change by dragging the control elements of the widget. Use the CHANGE callback of the widget to make the selected object follow manipulators transformations.
int AppSystemLogic::init()
{
// create a manipulator class instance and add it to the UI
gui = Gui::get();
WidgetManipulatorTranslatorPtr ManObjTranslator = WidgetManipulatorTranslator::create(gui);
gui->addChild(ManObjTranslator);
// add method to the widget as a callback
ManObjTranslator->addCallback(Gui::CALLBACK_INDEX::CHANGED, MakeCallback(this, &AppSystemLogic::ApplyTransform));
return 1;
}
// a callback method used to transform an object
void AppSystemLogic::ApplyTransform()
{
if(obj)
obj->setWorldTransform(ManObjTranslator->getTransform());
}Selecting Objects Using Mouse Cursor#
To select an object under the mouse cursor we should cast a ray from the cursor location in the view direction of the camera using the World::getIntersection() method, that will return an intersected object (if any):
ObjectPtr AppSystemLogic::GetNodeUnderCursor()
{
auto player = Game::getPlayer();
WorldIntersectionPtr intersection;
// get mouse coordinates
Math::ivec2 mouse = Input::getMouseCoord();
// cast a ray from the mouse cursor position in the direction of the camera 100 units away to detect and return any intersected objects
return World::getIntersection(player->getWorldPosition(), player->getDirectionFromScreen(mouse.x,mouse.y)*100,1,intersection);
}Putting it All Together#
Now let's put it all together and add a keyboard handler to switch the current manipulator. For example, let's use Z,X,C keys to select Translator, Rotator, Scaler Manipulators accordingly. Selected widget should be displayed on the screen where the object is located (have the same transformation).
- Create a new C++ project.
- Copy the code below and paste it to the corresponding source files in your project.
// AppSystemLogic.h
#include <UnigineLogic.h>
#include <UnigineWidgets.h>
#include <UniginePlayers.h>
class AppSystemLogic : public Unigine::SystemLogic
{
public:
AppSystemLogic();
virtual ~AppSystemLogic();
int init() override;
int update() override;
int postUpdate() override;
int shutdown() override;
// define auxiliary methods used for the project
void ApplyTransform();
Unigine::ObjectPtr GetNodeUnderCursor();
void SwitchManipulator(Unigine::WidgetManipulatorPtr CurrentManipulator);
private:
// define a pointer to access object parameters
Unigine::ObjectPtr obj;
// define a pointer to access UI
Unigine::GuiPtr gui;
// define a pointer to store transformation matrix of an active widget
Unigine::WidgetManipulatorPtr CurrentObjectManipulator;
// define pointers to display transformation matrix for each type of transform
Unigine::WidgetManipulatorTranslatorPtr ManObjTranslator;
Unigine::WidgetManipulatorRotatorPtr ManObjRotator;
Unigine::WidgetManipulatorScalerPtr ManObjScaler;
};// AppSystemLogic.cpp
#include <AppSystemLogic.h>
#include <UnigineApp.h>
#include <UnigineWidgets.h>
#include <UnigineGame.h>
#include <UnigineWorld.h>
#include <UniginePlayers.h>
#include <Math.h>
using namespace Unigine;
// System logic, it exists during the application life cycle.
// These methods are called right after corresponding system script's (UnigineScript) methods.
// callback method used to apply transformation according to users actions
void AppSystemLogic::ApplyTransform()
{
if(obj)
obj->setWorldTransform(CurrentObjectManipulator->getTransform());
}
// method used to find an object
ObjectPtr AppSystemLogic::GetNodeUnderCursor()
{
auto player = Game::getPlayer();
WorldIntersectionPtr intersection;
// find mouse position on the screen
Math::ivec2 mouse = Input::getMouseCoord();
// return an object intersected by the casted ray from the cursor position in the direction of the camera 100 units away
return World::getIntersection(player->getWorldPosition(), player->getDirectionFromScreen(mouse.x,mouse.y)*100,1,intersection);
}
// method used to switch manipulators
void AppSystemLogic::SwitchManipulator(WidgetManipulatorPtr CurrentManipulator)
{
// move to selected object and display chosen manipulator
CurrentManipulator->setTransform(obj->getWorldTransform());
CurrentManipulator->setHidden(false);
// hide other widget manipulators
CurrentObjectManipulator = CurrentManipulator;
if (ManObjTranslator != CurrentObjectManipulator)
ManObjTranslator->setHidden(true);
if (ManObjRotator != CurrentObjectManipulator)
ManObjRotator->setHidden(true);
if (ManObjScaler != CurrentObjectManipulator)
ManObjScaler->setHidden(true);
}
AppSystemLogic::AppSystemLogic()
{
}
AppSystemLogic::~AppSystemLogic()
{
}
int AppSystemLogic::init()
{
// Write here code to be called on engine initialization.
// create widget manipulators
gui = Gui::get();
ManObjTranslator = WidgetManipulatorTranslator::create(gui);
ManObjRotator = WidgetManipulatorRotator::create(gui);
ManObjScaler = WidgetManipulatorScaler::create(gui);
// add widgets to the UI
gui->addChild(ManObjTranslator);
gui->addChild(ManObjRotator);
gui->addChild(ManObjScaler);
// hide manipulators, so that they wouldn't appear after application initialization
ManObjTranslator->setHidden(true);
ManObjRotator->setHidden(true);
ManObjScaler->setHidden(true);
// add a callback to each widget manipulator
ManObjTranslator->addCallback(Gui::CALLBACK_INDEX::CHANGED, MakeCallback(this, &AppSystemLogic::ApplyTransform));
ManObjRotator->addCallback(Gui::CALLBACK_INDEX::CHANGED, MakeCallback(this, &AppSystemLogic::ApplyTransform));
ManObjScaler->addCallback(Gui::CALLBACK_INDEX::CHANGED, MakeCallback(this, &AppSystemLogic::ApplyTransform));
return 1;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// start of the main loop
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int AppSystemLogic::update()
{
// set projection and viewmodel for the each widget every frame
auto player = Game::getPlayer();
if (player)
{
ManObjTranslator->setProjection(player->getProjection());
ManObjRotator->setProjection(player->getProjection());
ManObjScaler->setProjection(player->getProjection());
ManObjTranslator->setModelview(player->getCamera()->getModelview());
ManObjRotator->setModelview(player->getCamera()->getModelview());
ManObjScaler->setModelview(player->getCamera()->getModelview());
}
// find object with a right-click
if (Input::isMouseButtonDown(Input::MOUSE_BUTTON::MOUSE_BUTTON_RIGHT))
{
obj = GetNodeUnderCursor();
}
// switch widgets on command with Z,X,C keys
if (obj)
{
if(CurrentObjectManipulator)
CurrentObjectManipulator->setTransform(obj->getWorldTransform());
if (Input::isKeyDown(Input::KEY::KEY_Z))
SwitchManipulator(ManObjTranslator);
if (Input::isKeyDown(Input::KEY::KEY_X))
SwitchManipulator(ManObjRotator);
if (Input::isKeyDown(Input::KEY::KEY_C))
SwitchManipulator(ManObjScaler);
}
// Write here code to be called before updating each render frame.
return 1;
}
int AppSystemLogic::postUpdate()
{
// Write here code to be called after updating each render frame.
return 1;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// end of the main loop
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int AppSystemLogic::shutdown()
{
// Write here code to be called on engine shutdown.
return 1;
}