GameIntersection Class
Warning
The scope of applications for UnigineScript is limited to implementing materials-related logic (material expressions, scriptable materials, brush materials). Do not use UnigineScript as a language for application logic, please consider C#/C++ instead, as these APIs are the preferred ones. Availability of new Engine features in UnigineScipt (beyond its scope of applications) is not guaranteed, as the current level of support assumes only fixing critical issues.
Stores the result of the engine.game.getIntersection() function: the point where the intersection with an obstacle has been occurred.
Usage Example#
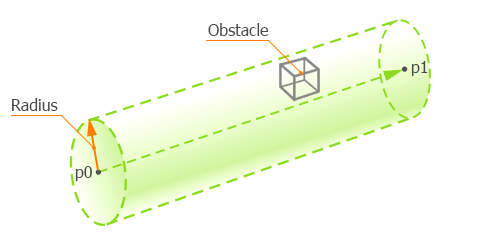
The following example shows how you can get the intersection point (vec3) of the cylinder between two points with an obstacle. In this example the cylinder is an invisible traced cylinder from the point of the camera (vec3 p0) to the point of the mouse pointer (vec3 p1) with the specific radius. The executing sequence is the following:
- Define and initialize two points (p0 and p1) by using the Unigine::getPlayerMouseDirection() function from core/scripts/utils.h.
- Create an instance of the GameIntersection class to get the intersection point coordinates.
- Check, if there is a intersection with an obstacle. The engine.game.getIntersection() function returns an intersected obstacle when the obstacle appears in the area of the cylinder.
- After that GameIntersection instance gets the point of the nearest intersection point and you can get it by using the getPoint() function.
Source code (UnigineScript)
#include <core/scripts/utils.h>
/* ... */
// define two vec3 coordinates
vec3 p0,p1;
// get the mouse direction from camera (p0) to cursor pointer (p1)
Unigine::getPlayerMouseDirection(p0,p1);
// create an instance of the GameIntersection class
GameIntersection intersection = new GameIntersection();
// try to get the intersection with an obstacle.
// cylinder has radius 0.1f, intersection mask equals to 1
Obstacle obstacle = engine.game.getIntersection(p0,p1,0.1f, 1, intersection);
// check, if the intersection of mouse direction with any obstacle was occurred;
if(obstacle !=NULL)
{
// show the coordinates of the intersection in console
log.message("The intersection with obstacle was here: %s\n", typeinfo(intersection.getPoint()));
}
/* ... */GameIntersection Class
Members
static GameIntersection ( ) #
The GameIntersection constructor.void setPoint ( Vec3 point ) #
Sets new coordinates of the intersection point.Arguments
- Vec3 point - Coordinates of the intersection point.
Vec3 getPoint ( ) #
Returns coordinates of the intersection point.Return value
Coordinates of the intersection point.Last update:
2020-07-31
Help improve this article
Was this article helpful?
(or select a word/phrase and press Ctrl+Enter)