生成物理对象
We need some geometric primitives that the player can move around the Play Area and shoot at. Let's generate them via code.我们需要一些几何元素,玩家可以移动游戏区域和射击。让我们通过代码生成它们。
A primitive should have a body and a shape to collide with the Player Character and be affected by gravity. We have implemented interaction with bullets via Intersections at the previous step, so we should set the BulletIntersection bit for the object's Intersection mask.一个基元应该有一个 body 和一个 shape 以与玩家角色发生碰撞并受重力影响。 我们在上一步已经通过 Intersections 实现了与子弹的交互,因此我们应该为对象的 Intersection 掩码设置 BulletIntersection 位。
When the robot moves fast and the application framerate is low, the character will be teleported each frame and may go through physical objects due to discrete collision detection. To avoid this we are going to use continuous collision detection.当机器人快速移动且应用程序帧率较低时,角色将每帧被传送,并且由于离散碰撞检测可能会穿过物理对象。 为了避免这种情况,我们将使用 连续碰撞检测。
-
Create a new C++ component in your IDE and call it ObjectGenerator. Copy the following code to the corresponding files and save the solution. This component generates the physical objects and places them in the world.在您的 IDE 中创建一个新的 C++ 组件,并将其命名为 ObjectGenerator。 将以下代码复制到相应的文件并保存解决方案。 该组件生成物理对象并将它们放置在世界中。
ObjectGenerator.h (C++)#include <UnigineComponentSystem.h> #include <UnigineGame.h> #pragma once class ObjectGenerator : public Unigine::ComponentBase { public: COMPONENT_DEFINE(ObjectGenerator, ComponentBase); COMPONENT_INIT(init, 1); // 1st initialization order protected: void init(); };ObjectGenerator.cpp (C++)#include "ObjectGenerator.h" #include <UniginePrimitives.h> using namespace Unigine; REGISTER_COMPONENT(ObjectGenerator); void ObjectGenerator::init() { // cube ObjectMeshDynamicPtr box = Primitives::createBox(Math::vec3(1.0f)); box->setTriggerInteractionEnabled(1); box->setIntersection(1, 0); box->setIntersectionMask(0x00000080, 0); // check the BulletIntersection bit box->setWorldTransform(translate(Math::Vec3(0.5f, 7.5f, 1.0f))); box->setMaterialPath("materials/mesh_base_0.mat", "*"); box->setName("box"); Unigine::BodyRigidPtr bodyBox = BodyRigid::create(box); ShapeBoxPtr shapeBox = ShapeBox::create(bodyBox, Math::vec3(1.0f)); ShapeSphere::create(bodyBox, 0.5f); bodyBox->setShapeBased(0); bodyBox->setMass(2.0f); // sphere ObjectMeshDynamicPtr sphere = Primitives::createSphere(0.5f, 9, 32); sphere->setTriggerInteractionEnabled(1); sphere->setIntersection(1, 0); sphere->setIntersectionMask(0x00000080, 0); // check the BulletIntersection bit sphere->setWorldTransform(translate(Math::Vec3(4.5f, 5.5f, 1.0f))); sphere->setMaterialPath("materials/mesh_base_1.mat", "*"); sphere->setName("sphere"); BodyRigidPtr bodySphere = BodyRigid::create(sphere); ShapeSphere::create(bodySphere, 0.5f); bodySphere->setShapeBased(0); bodySphere->setMass(2.0f); // capsule ObjectMeshDynamicPtr capsule = Primitives::createCapsule(0.5f, 1.0f, 9, 32); capsule->setTriggerInteractionEnabled(1); capsule->setIntersection(1, 0); capsule->setIntersectionMask(0x00000080, 0); // check the BulletIntersection bit capsule->setWorldTransform(translate(Math::Vec3(4.5f, 0.5f, 3.0f))); capsule->setMaterialPath("materials/mesh_base_2.mat", "*"); capsule->setName("capsule"); BodyRigidPtr bodyCapsule = BodyRigid::create(capsule); ShapeCapsule::create(bodyCapsule, 0.5f, 1.0f); bodyCapsule->setShapeBased(0); bodyCapsule->setMass(2.0f); }注意Do not change the size of an object after the creation. The physics doesn't support scaling nodes with Body attached. 创建后不要更改对象的大小。 物理不支持附加 Body 的缩放节点。 - Build and run the solution in your IDE to generate a property file for the component.构建和运行的解决方案在IDE生成组件的属性文件。
- Switch back to the UnigineEditor and create a new Dummy Node, rename it to "object_generator", and place it somewhere in the world.切换回UnigineEditor并创建一个新的Dummy Node,重命名它为"object_generator",它在世界上的地位。
- Attach the created ObjectGenerator component to the "object_generator" node to make it generate physical objects on the initialization.把ObjectGenerator组件创建"object_generator"节点生成物理对象的初始化。
-
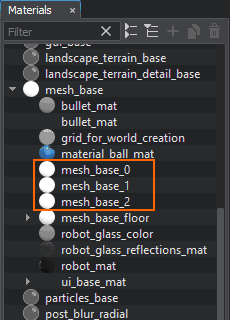
Create 3 new materials in the UnigineEditor: in the Materials window, right-click the mesh_base material and choose Create Child. By default, the created materials are named as specified in the previous code snippet (mesh_base_*). Move the materials to the data/materials folder of your project (create this folder if it doesn't exist).在 UnigineEditor 中创建 3 个新材质:在 Materials 窗口中,右键单击 mesh_base 材质并选择 Create Child。 默认情况下,创建的材质按照前面的代码片段 (mesh_base_*) 中的指定命名。 将材质移动到项目的 data/materials 文件夹(如果该文件夹不存在,请创建此文件夹)。
-
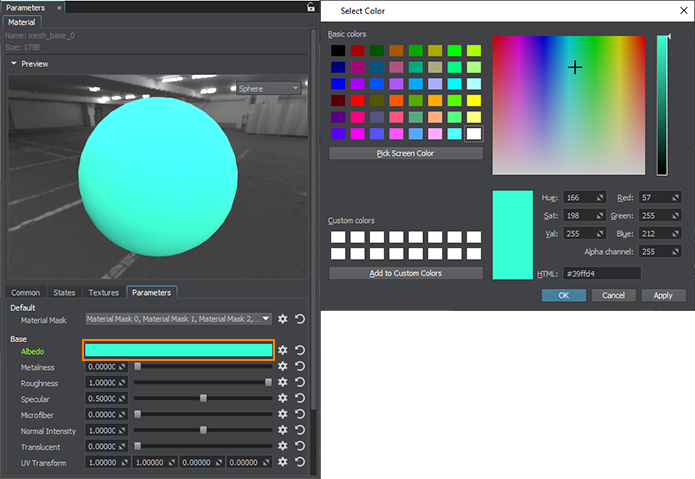
Select materials one by one in the Materials window and in the Parameters window switch to the Parameters tab and click on the color field near Albedo to choose different colors for the objects via the color picker.在Materials窗口中一一选择材质,在Parameters窗口切换到Parameters选项卡点击Albedo附近的色域进行选择 通过颜色选择器为对象设置不同的颜色。
- Save changes to the world via Ctrl + S.通过Ctrl + S拯救世界的变化。
- Run the project in your IDE to see the spawned physical objects in the world.在IDE运行项目世界上看到了实物。
