Asset Types
There are a number of file types supported by the UNIGINE assets system. This page contains a categorized list of these file types along with a brief description.
Geometry and Animation
Mesh is the basic unit, that consists of a set of polygons and is used to create geometry for worlds in a UNIGINE project.
Some meshes can be animated, apart from a set of polygons representing its surfaces, such mesh has a hierarchical set of interconnected bones (a skeleton or a rig) which can be used to animate the vertices of the polygons. Another way to animate a model is to create morph targets (or blend shapes), these are "deformed" versions of a mesh, stored as a series of vertex positions. In each key frame of an animation, the vertices are interpolated between these stored positions.

You can create 3D models, rigs and animations in an external modeling application (3DSMax, Maya, Softimage, etc.), and then import them to your UNIGINE project via the Asset Browser.
| Format | Description |
|---|---|
| .fbx |
A 3D model or a scene created in an external 3D modeling application. It can contain static meshes, skeletal meshes, animations, morph targets, light sources, and cameras. |
| .dae |
A 3D model or a scene created in an external 3D modeling application and stored in DAE format (COLLADA). It can contain static meshes, skeletal meshes, animations, morph targets, light sources, and cameras. Import settings for DAE files are the same as the ones used for FBX import. |
| .3ds |
A 3D model or a scene created in an external 3D modeling application and stored in 3DS format (3D MAX). It can contain static meshes, skeletal meshes, animations, morph targets, light sources, and cameras. Import settings for 3DS files are the same as the ones used for FBX import. |
| .obj |
Static polygonal geometry stored in OBJ format — namely, the position of each vertex, the UV position of each texture coordinate vertex, vertex normals, and the faces that make each polygon defined as a list of vertices, and texture vertices. The file format is open and has been adopted by other 3D graphics application vendors. Notice
If you want to import your 3d model with all materials assigned, you should import all corresponding material library assets (*.mtl files) either prior to importing the *.obj file or together with it. |
| .mesh |
Built-in file format, that describes static and skinned geometry. It supports multiple surfaces and variable number of morph targets (blend shapes) for each surface, as well as multiple named animations stored in the single file. |
| .anim |
Built-in file format, that describes skinned animation. It is used together with *.mesh file that contains a bind pose. Thus, you can have a single skinned mesh (*.mesh) and multiple animations for it. |
Textures
Textures are images that are commonly used in materials. When a material is applied to a surface, textures are mapped to it. They can be either applied directly, as albedo textures, for instance, used as masks, or the values of the texture's pixels can be used for other calculations. Textures can also be used directly, e.g., as environment cubemaps, or to draw a projection of a Projected Light Source.
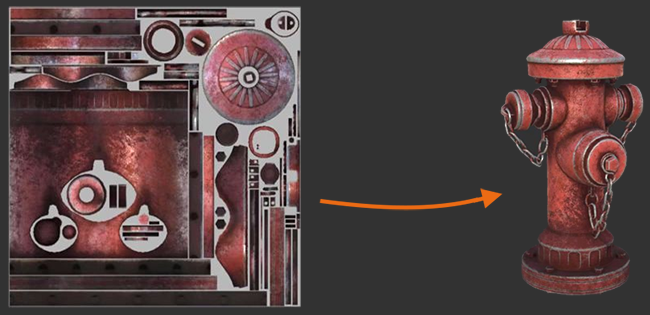
Textures are generally created using an external image-editing application, such as GIMP or Photoshop, and then imported via the Asset Browser. Some textures, such as render textures, are generated by the UNIGINE Engine. They generally take some information from the scene and render it to a texture to be used elsewhere.
Several textures can be used in a single material for different purposes. For instance, a material may have an albedo texture, an ambient occlusion texture, a normal map, etc. In addition, there may be a map for the Emissive and Roughness stored in the alpha channels of one or more of these textures.
UNIGINE supports the most popular bitmap texture formats (see the table below) along with the following features:
- 8, 16 and 32 bit precision per channel.
- Alpha channel.
- Baked MIP-levels.
| Format | Description |
|---|---|
| .png |
Image file stored in the Portable Network Graphic (PNG) format; contains a bitmap of indexed colors under a lossless compression; commonly used to store graphics for Web images. |
| .jpg |
Image file stored in the JPG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) format using lossy compression. |
| .tiff |
Image file stored in the TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) format using losless compression. |
| .dds |
File in (DirectDraw Surface) format, contains compressed or uncompressed image data, which is optimal for GPUs. |
| .tga |
Image in raster graphic file format designed by Truevision; supports 8, 16, 24, or 32 bits per pixel at a maximum of 24 bits for RGB colors and 8-bit alpha channel. |
| .rgb, .rgba |
Bitmap in RGB/RGBA format. |
| .psd |
Image file created by Adobe Photoshop, a professional image-editing program; may include image layers, adjustment layers, layer masks, annotation notes, file information, keywords, and other Photoshop-specific elements. |
| .hdr |
High Dynamic Range image. These are most commonly used for environment maps. |
| .pgm |
Netpbm grayscale image. |
| .ppm |
Image file stored in the PPM (Portable Pixmap) format. |
| .sgi |
Image file stored in the SGI (Silicon Graphics Image) format. |
To learn more about importing textures, see the Texture Import Guide.
Materials
Material defines how the surface, to which it is assigned, will look like: its interaction with lights, reflection parameters, etc. A material asset is generally linked to several texture assets.
The list of supported material assets includes the following:
| Format | Description |
|---|---|
| .basemat |
Built-in type representing a base material, from which other materials can be inherited. |
| .mat |
Built-in type representing a user material inherited from the base one. |
| .mtl |
Material template library MTL file, that stores description of materials for 3D models in OBJ format. Notice
An *.mtl file should be imported together with a corresponding *.obj file referring to it. |
When materials are imported along with a 3D model, only the following source data will be used (if defined):
- Textures:
- Diffuse (albedo) texture
- Normal map or bump map
- Specular texture
- Light map
- Parameters:
- Diffuse color
- Specular color and power
- Emission color
Sound and Video Files
Sound assets - are the key resources for creating the proper feeling of immersion in the virtual world. UNIGINE supports virtually the unlimited number of sound sources
Either as mono or stereo files, compressed or not, they can be quickly imported into your project.
In the table below you'll find types of sound and video assets supported by UNIGINE.
Scripts
Scripts are an essential part of your project representing application logic. UNIGINE has its ows scripting language - UnigineScript. It is designed to make coding easy-to-use even for junior programmers and at the same time provide the most optimal Engine usage. Scripts are platform-independent and do not require compilation.

This type of assets can be created and edited in a plain text-editor. You can add scripts to your project via the Asset Browser
| Format | Description |
|---|---|
| .h |
Built-in type representing a header-file for a script written in UnigineScript. |
| .cpp |
Built-in type representing a script written in UnigineScript. |
| .usc |
Built-in type representing a script written in UnigineScript. |
Presets
UnigineEditor allows you to save various presets - configurations of different settings (e.g. rendering settings, gravity, sound velocity, volumes of sound sources, etc.). This type of assets can be used to configure worlds within your project.
| Format | Description |
|---|---|
| .render |
Built-in type that determines a configuration of rendering settings for a world. |
| .physics |
Built-in type that determines a configuration of physics simulation settings for a world. |
| .sound |
Built-in type that determines a configuration of sound settings for a world. |
Other Asset Types
| Format | Description |
|---|---|
| .world |
Built-in type describing a UNIGINE world (scene). One project can include several worlds. So, there is no need to create a separate project for each world. Created in the UnigineEditor. |
| .node |
Built-in type describing any Node (or a hierarchy of Nodes) of the UNIGINE's virtual world. Created in the UnigineEditor or at runtime via the code. |
| .prop |
Built-in type describing a property. A property is a "material" for application logic. It specifies the way how the object will behave and interact with other objects and the scene environment. |
| .landscape |
Built-in type, that stores generation parameters used by the Landscape Tool to generate a TerrainGlobal object. Created in the Landscape Tool. |
| .track |
Built-in type, that contains the sequence of the parameters animated with keyframes along the timeline. Created in the Tracker Tool. |
| .ttf |
The font in TTF (True Type Font) format. As a raster font, it can be scaled to any size without quality loss or pixelation, and the stored image appears the same when printed as it does on-screen. You can use any existing TTF font or create a new one. |
| .path |
The path is a spline along which an object can be moved. Such splines can be created, for example, in 3ds Max or via the API, using the Path class and then saved to the *.path file. |