Volume Projected
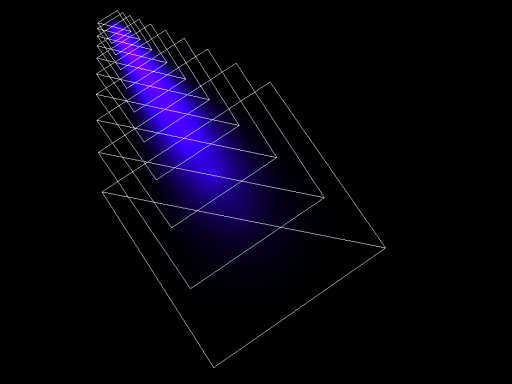
The Volume Projected object is used to create light beams from directional light sources, such as car headlights, searchlights or beacon light. It can also be animated to simulate a flow of particles that moves from the light source or even swirls. Only a volume proj material can be assigned to it.

Volume Projected is rendered as a simple particle system. It is a number of Billboards, where each following Billboard is bigger than the previous one.
See also#
- The ObjectVolumeProj class to edit Volume Projected objects via API
Creating a Volume Projected Object#
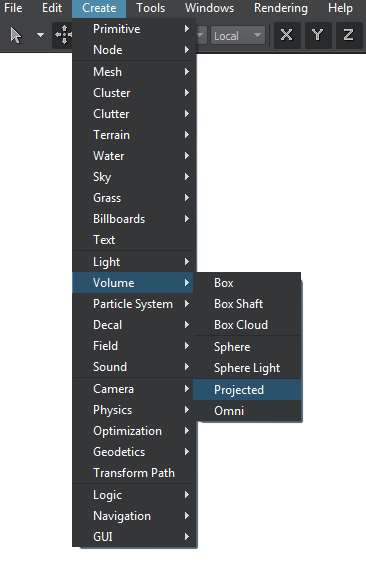
To create a Volume Projected object, perform the following steps:
-
On the Menu bar, click Create -> Volume -> Projected.
- Place the Volume Projected object somewhere in the world.
- Specify the Volume Projected object parameters.
Volume Projected Parameters#
In the Volume Projected section (Parameters window -> Node tab), you can adjust the following parameters of the Volume Projected object:
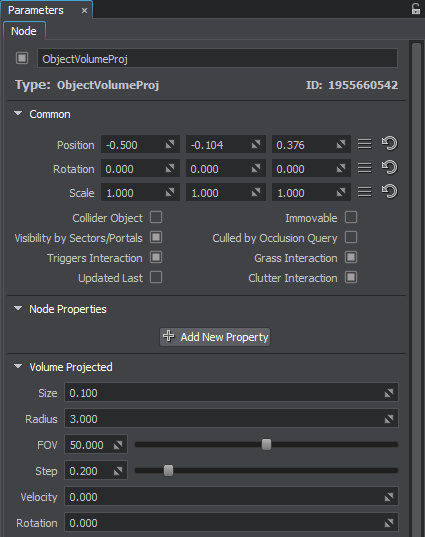
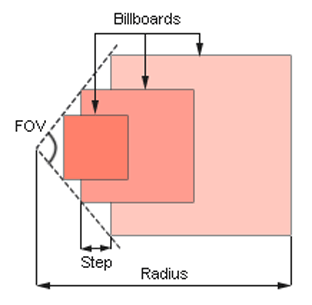
| Size | Size of the smallest Billboard in units. By the minimum value of 0, Volume Projected is not rendered at all. |
|---|---|
| Radius | Length of the light beam along the Z axis, in units. |
| FOV |
Width of the light beam. It is specified as the angle of the beam cone (in degrees).
|
| Step |
Distance between neighboring Billboards.
|
| Velocity | Velocity with which Billboards move to the end of the beam (along the Z axis). |
| Rotation |
Angle of Billboards rotation (in degrees). This angle is set for the Billboard at the end of the beam.

Positive rotation angle
|
The information on this page is valid for UNIGINE 2.19 SDK.