Unigine::JointSuspension Class
| Header: | #include <UniginePhysics.h> |
| Inherits from: | Joint |
Warning
This joint type is deprecated and will be removed in the upcoming releases. It is recommended to use the Wheel Joint instead.
This class is used to create a suspension joint. The bodies that represent both a frame and a wheel must be rigid bodies.
Example#
The following code illustrates connection of two rigid bodies (frame and wheel) using a suspension joint.
Source code (C++)
include <UniginePhysics.h>
/* .. */
JointSuspensionPtr joint = JointSuspension::create(frame, wheel);
// setting joint anchor coordinates
joint->setWorldAnchor(wheel->getObject()->getWorldTransform() * Vec3(0.0f));
// setting joint axes coordinates
joint->setWorldAxis0(vec3(0.0f,0.0f,1.0f));
joint->setWorldAxis1(vec3(0.0f,1.0f,0.0f));
// setting linear damping and spring rigidity
joint->setLinearDamping(2.0f);
joint->setLinearSpring(200.0f);
// setting lower and upper suspension ride limits [-0.5; 0.0]
joint->setLinearLimitFrom(-0.5f);
joint->setLinearLimitTo(0.0f);
// setting target suspension height
joint->setLinearDistance(0.5f);
// setting maximum angular velocity and torque
joint->setAngularVelocity(-20.0f);
joint->setAngularTorque(10.0f);
// setting common joint constraint parameters
joint->setLinearRestitution(0.2f);
joint->setAngularRestitution(0.2f);
joint->setLinearSoftness(0.2f);
joint->setAngularSoftness(0.2f);
// setting number of iterations
joint->setNumIterations(8);See Also#
-
A set of UnigineScript API samples located in the <UnigineSDK>/data/samples/physics/ folder:
- car_00
- car_01
- car_02
JointSuspension Class
Members
float getCurrentLinearDistance() const#
Returns the current suspension compression.
Return value
Current suspension height, in units.float getCurrentAngularVelocity() const#
Returns the current velocity of wheel rotation.
Return value
Current current velocity, in radians per second.void setAngularVelocity ( float velocity ) #
Sets a new target velocity of wheel rotation.
Arguments
- float velocity - The target velocity in radians per second.
float getAngularVelocity() const#
Returns the current target velocity of wheel rotation.
Return value
Current target velocity in radians per second.void setAngularTorque ( float torque ) #
Sets a new maximum torque of the attached angular motor. 0 means that the motor is not attached.
Arguments
- float torque - The maximum torque. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead. 0 detaches the motor.
float getAngularTorque() const#
Returns the current maximum torque of the attached angular motor. 0 means that the motor is not attached.
Return value
Current maximum torque. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead. 0 detaches the motor.void setAngularDamping ( float damping ) #
Sets a new angular damping of the joint (wheel rotation damping).
Arguments
- float damping - The angular damping. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead.
float getAngularDamping() const#
Returns the current angular damping of the joint (wheel rotation damping).
Return value
Current angular damping. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead.void setLinearSpring ( float spring ) #
Sets a new rigidity coefficient of the suspension. 0 means that the suspension is not attached.
Arguments
- float spring - The rigidity coefficient. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead. 0 detaches the suspension.
float getLinearSpring() const#
Returns the current rigidity coefficient of the suspension. 0 means that the suspension is not attached.
Return value
Current rigidity coefficient. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead. 0 detaches the suspension.void setLinearLimitTo ( float to ) #
Sets a new high limit of the suspension ride. This limit specifies how far a connected body can move along the joint axis.
Arguments
- float to - The high limit in units.
float getLinearLimitTo() const#
Returns the current high limit of the suspension ride. This limit specifies how far a connected body can move along the joint axis.
Return value
Current high limit in units.void setLinearLimitFrom ( float from ) #
Sets a new low limit of the suspension ride. This limit specifies how far a connected body can move along the joint axis.
Arguments
- float from - The low limit in units.
float getLinearLimitFrom() const#
Returns the current low limit of the suspension ride. This limit specifies how far a connected body can move along the joint axis.
Return value
Current low limit in units.void setLinearDistance ( float distance ) #
Sets a new target height of the suspension.
Arguments
- float distance - The height, in units.
float getLinearDistance() const#
Returns the current target height of the suspension.
Return value
Current height, in units.void setLinearDamping ( float damping ) #
Sets a new linear damping of the suspension.
Arguments
- float damping - The linear damping. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead.
float getLinearDamping() const#
Returns the current linear damping of the suspension.
Return value
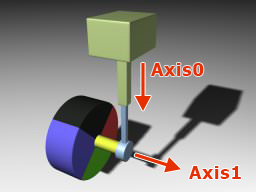
Current linear damping. If a negative value is provided, 0 will be used instead.void setWorldAxis0 ( const Math::vec3& axis0 ) #
Sets a new suspension axis in the world coordinates.
Arguments
- const Math::vec3& axis0 - The suspension axis in the world coordinates.
Math::vec3 getWorldAxis0() const#
Returns the current suspension axis in the world coordinates.
Return value
Current suspension axis in the world coordinates.void setWorldAxis1 ( const Math::vec3& axis1 ) #
Sets a new wheel spindle axis in the world coordinates.
Arguments
- const Math::vec3& axis1 - The wheel spindle axis in the world coordinates.
Math::vec3 getWorldAxis1() const#
Returns the current wheel spindle axis in the world coordinates.
Return value
Current wheel spindle axis in the world coordinates.void setAxis00 ( const Math::vec3& axis00 ) #
Sets a new coordinates of suspension axis, along which a wheel moves vertically. This is a shock absorber.
Arguments
- const Math::vec3& axis00 - The suspension axis, in the world coordinates.
Math::vec3 getAxis00() const#
Returns the current coordinates of suspension axis, along which a wheel moves vertically. This is a shock absorber.
Return value
Current suspension axis, in the world coordinates.void setAxis10 ( const Math::vec3& axis10 ) #
Sets a new wheel spindle axis in coordinates of the frame (body 0): an axis around which a wheel rotates when moving forward (or backward).
Arguments
- const Math::vec3& axis10 - The wheel spindle axis in coordinates of the frame (body 0).
Math::vec3 getAxis10() const#
Returns the current wheel spindle axis in coordinates of the frame (body 0): an axis around which a wheel rotates when moving forward (or backward).

Return value
Current wheel spindle axis in coordinates of the frame (body 0).void setAxis11 ( const Math::vec3& axis11 ) #
Sets a new wheel spindle axis in coordinates of the wheel (body 1): an axis around which a wheel rotates when steering.

Arguments
- const Math::vec3& axis11 - The wheel spindle axis in coordinates of the wheel (body 1).
Math::vec3 getAxis11() const#
Returns the current wheel spindle axis in coordinates of the wheel (body 1): an axis around which a wheel rotates when steering.

Return value
Current wheel spindle axis in coordinates of the wheel (body 1).static JointSuspensionPtr create ( ) #
Constructor. Creates a suspension joint with an anchor at the origin of the world coordinates.static JointSuspensionPtr create ( const Ptr<Body> & body0, const Ptr<Body> & body1 ) #
Constructor. Creates a suspension joint connecting two given bodies. An anchor is placed between centers of mass of the bodies.Arguments
- const Ptr<Body> & body0 - Frame to be connected with the joint.
- const Ptr<Body> & body1 - Wheel to be connected with the joint.
static JointSuspensionPtr create ( const Ptr<Body> & body0, const Ptr<Body> & body1, const Math::Vec3 & anchor, const Math::vec3 & axis0, const Math::vec3 & axis1 ) #
Constructor. Creates a suspension joint connecting two given bodies with specified suspension and spindle axis coordinates and an anchor placed at specified coordinates.Arguments
The information on this page is valid for UNIGINE 2.18.1 SDK.
Last update:
2024-08-07
Help improve this article
Was this article helpful?
(or select a word/phrase and press Ctrl+Enter)