Unigine::TextureRamp Class
| Header: | #include <UnigineTextures.h> |
Interface for handling ramp textures. This class lets the user store 2d curves in a form of a texture (convert vectors to raster data).
Ramp textures can be used for color variation in the particles_base material of Particle Systems or in other custom materials.
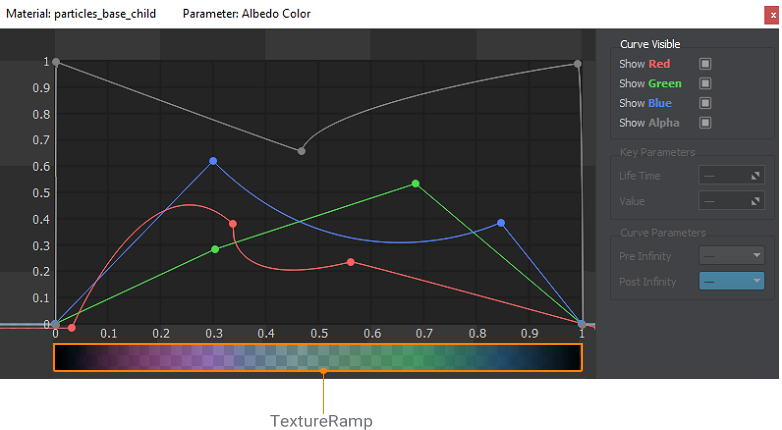
You can set up to 4 channels for the ramp texture.
TextureRamp Class
Members
Ptr<Texture> getTexture() const#
Returns the current new texture and updates hashes for curves, if required. Returns a pointer to the texture or null if the texture was not created.
Return value
Current new texture.void setNumChannels ( int channels ) #
Sets a new number of channels for the texture.
Arguments
- int channels - The number of texture channels.
int getNumChannels() const#
Returns the current number of channels for the texture.
Return value
Current number of texture channels.void setResolution ( int resolution ) #
Sets a new width resolution for the texture.
Arguments
- int resolution - The texture width resolution.
int getResolution() const#
Returns the current width resolution for the texture.
Return value
Current texture width resolution.void setFlags ( int flags ) #
Sets a new texture flags.
Arguments
- int flags - The texture flags.
int getFlags() const#
Returns the current texture flags.
Return value
Current texture flags.bool isDefaultAll() const#
Returns the current value indicating if the values of all curve channels are the default ones which were previously set via setDefaultCurve.
Return value
true if the values of all curve channels are the default ones which were previously set via setDefaultCurve; otherwise false.Event<> getEventChanged() const#
event triggered on changing the ramp texture. You can subscribe to events via
connect()
and unsubscribe via
disconnect(). You can also use
EventConnection
and
EventConnections
classes for convenience (see examples below).
The event handler signature is as follows: myhandler(Notice
For more details see the Event Handling article.
Usage Example
Source code (C++)
// implement the Changed event handler
void changed_event_handler()
{
Log::message("\Handling Changed event\n");
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 1. Multiple subscriptions can be linked to an instance of the EventConnections
// class that you can use later to remove all these subscriptions at once
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// create an instance of the EventConnections class
EventConnections changed_event_connections;
// link to this instance when subscribing to an event (subscription to various events can be linked)
publisher->getEventChanged().connect(changed_event_connections, changed_event_handler);
// other subscriptions are also linked to this EventConnections instance
// (e.g. you can subscribe using lambdas)
publisher->getEventChanged().connect(changed_event_connections, []() {
Log::message("\Handling Changed event (lambda).\n");
}
);
// ...
// later all of these linked subscriptions can be removed with a single line
changed_event_connections.disconnectAll();
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 2. You can subscribe and unsubscribe via an instance of the EventConnection
// class. And toggle this particular connection off and on, when necessary.
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// create an instance of the EventConnection class
EventConnection changed_event_connection;
// subscribe to the Changed event with a handler function keeping the connection
publisher->getEventChanged().connect(changed_event_connection, changed_event_handler);
// ...
// you can temporarily disable a particular event connection to perform certain actions
changed_event_connection.setEnabled(false);
// ... actions to be performed
// and enable it back when necessary
changed_event_connection.setEnabled(true);
// ...
// remove subscription to the Changed event via the connection
changed_event_connection.disconnect();
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 3. You can add EventConnection/EventConnections instance as a member of the
// class that handles the event. In this case all linked subscriptions will be
// automatically removed when class destructor is called
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class handling the event
class SomeClass
{
public:
// instance of the EventConnections class as a class member
EventConnections e_connections;
// A Changed event handler implemented as a class member
void event_handler()
{
Log::message("\Handling Changed event\n");
// ...
}
};
SomeClass *sc = new SomeClass();
// ...
// specify a class instance in case a handler method belongs to some class
publisher->getEventChanged().connect(sc->e_connections, sc, &SomeClass::event_handler);
// ...
// handler class instance is deleted with all its subscriptions removed automatically
delete sc;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 4. You can subscribe and unsubscribe via the handler function directly
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// subscribe to the Changed event with a handler function
publisher->getEventChanged().connect(changed_event_handler);
// remove subscription to the Changed event later by the handler function
publisher->getEventChanged().disconnect(changed_event_handler);
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 5. Subscribe to an event saving an ID and unsubscribe later by this ID
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// define a connection ID to be used to unsubscribe later
EventConnectionId changed_handler_id;
// subscribe to the Changed event with a lambda handler function and keeping connection ID
changed_handler_id = publisher->getEventChanged().connect([]() {
Log::message("\Handling Changed event (lambda).\n");
}
);
// remove the subscription later using the ID
publisher->getEventChanged().disconnect(changed_handler_id);
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 6. Ignoring all Changed events when necessary
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// you can temporarily disable the event to perform certain actions without triggering it
publisher->getEventChanged().setEnabled(false);
// ... actions to be performed
// and enable it back when necessary
publisher->getEventChanged().setEnabled(true);Return value
Event reference.static TextureRampPtr create ( int num_channels, int resolution, int flags ) #
Sets resolution, number of channels and texture flags for this TextureRamp instance. The pointer to the ramp texture is set to null and curves are marked for an update.Arguments
- int num_channels - Number of texture channels.
- int resolution - Width resolution of the ramp texture.
- int flags - Texture flags.
static TextureRampPtr create ( const Ptr<TextureRamp> & texture_ramp ) #
Ramp texture constructor. Creates a new ramp texture by copying a given source ramp texture.Arguments
- const Ptr<TextureRamp> & texture_ramp - Pointer to a new ramp texture.
TextureRamp ( ) #
void releaseTexture ( ) #
Deletes the texture and its pointer.void copy ( const Ptr<TextureRamp> & src_texture_ramp ) #
Copies the data of a source ramp texture to the texture.Arguments
- const Ptr<TextureRamp> & src_texture_ramp - Source ramp texture.
Ptr<TextureRamp> clone ( ) const#
Duplicates the ramp texture and returns a pointer to the copy.Ptr<Curve2d> getCurve ( int channel ) const#
Returns a pointer to the Curve2d for the specified channel.Arguments
- int channel - Required channel.
Return value
Pointer to a Curve2d object.void setDefaultCurve ( const Ptr<Curve2d> & default_curve ) #
Resets a curve to a default one.Arguments
void setDefaultCurve ( int channel, const Ptr<Curve2d> & default_curve ) #
Resets a curve for the given channel to a default one.Arguments
- int channel - R, G, B, or A channel set by the corresponding value from 0 to 3.
- const Ptr<Curve2d> & default_curve - A curve to be used as the default one.
bool isDefault ( int channel ) const#
Returns a value indicating if the value of the given curve channel is the default one which was previously set via setDefaultCurve.Arguments
- int channel - R, G, B, or A channel set by the corresponding value from 0 to 3.
Return value
true if the curve value is the default one set via setDefaultCurve, otherwise false.void save ( const Ptr<Xml> & xml ) #
Saves the ramp texture data to the given Xml node.Arguments
void save ( const Ptr<Json> & json ) const#
Saves the ramp texture data to the given Json class instance.Arguments
void load ( const Ptr<Xml> & xml ) #
Loads the ramp texture data from the given Xml node.Arguments
void load ( const Ptr<Json> & json ) #
Loads the ramp texture data from the given Json class instance.Arguments
void saveState ( const Ptr<Stream> & stream ) const#
Saves the state of the ramp texture into a binary stream.Example using saveState() and restoreState() methods:
Source code (C++)
// initialize a node and set its state
//...//
// save state
BlobPtr blob_state = Blob::create();
ramp->saveState(blob_state);
// change state
//...//
// restore state
blob_state->seekSet(0); // returning the carriage to the start of the blob
ramp->restoreState(blob_state);Arguments
void restoreState ( const Ptr<Stream> & stream ) const#
Restores the state of the ramp texture from the binary stream.Example using saveState() and restoreState() methods:
Source code (C++)
// initialize a node and set its state
//...//
// save state
BlobPtr blob_state = Blob::create();
ramp->saveState(blob_state);
// change state
//...//
// restore state
blob_state->seekSet(0); // returning the carriage to the start of the blob
ramp->restoreState(blob_state);Arguments
The information on this page is valid for UNIGINE 2.18.1 SDK.
Last update:
2024-04-19
Help improve this article
Was this article helpful?
(or select a word/phrase and press Ctrl+Enter)