管理游戏规则
Let's create the LevelManager component to manage game rules, level states and the User Interface. The manager creates a graphical user interface and shows the time left until the game is over. It also checks and shows the number of objects left to clear away from the Play Area.让我们创建 LevelManager 组件来管理游戏规则、关卡状态和用户界面。 管理器创建一个图形用户界面,并显示游戏结束前的剩余时间。 它还检查并显示离开游戏区域的剩余物体数量。
Step 1. Set Up Timer and Game UI步骤1。设置定时器和游戏界面#
A node with the LevelManager component assigned should be present in the world for rules to take effect. It will manage the timer and update the widget user interface for the game.分配了 LevelManager 组件的节点应该存在于世界中,以使规则生效。 它将管理计时器并更新游戏的 widget 用户界面。
- Create a new C++ component and call it LevelManager.创建一个新的 C++ 组件 并将其命名为 LevelManager。
-
Write the following code in an IDE and save the solution. Build and run the solution to generate a property file for the component.IDE中编写以下代码并保存解决方案。构建和运行的解决方案组件生成一个属性文件。
注意Take note that the LevelManager component's init() method is set to be called in the 2nd order to make sure it is initialized after the ObjectGenerator component which creates and parents all physical objects to it (ObjectGenerator's initialization order is set to 1st).请注意,LevelManager 组件的 init() 方法设置为按 2nd 顺序调用,以确保它是 在 ObjectGenerator 组件之后初始化,该组件创建所有物理对象并将其作为父对象(ObjectGenerator 的初始化顺序设置为 1st)。LevelManager.h (С++)#pragma once #include <UnigineComponentSystem.h> #include <UnigineWidgets.h> #include <UnigineGame.h> #include <UnigineString.h> class LevelManager : public Unigine::ComponentBase { public: // declare constructor and destructor for our class and define a property name. COMPONENT_DEFINE(LevelManager, ComponentBase) // declare methods to be called at the corresponding stages of the execution sequence COMPONENT_INIT(init, 2); // 2nd initialization order COMPONENT_UPDATE(update); COMPONENT_SHUTDOWN(shutdown); // level timer PROP_PARAM(Float, timer, 100.0f); void decPhysicalObjectsNum(); void setEndGameCallback(Unigine::CallbackBase *callback) { endGameEvent = callback; } protected: void init(); void update(); void shutdown(); void initGUI(); private: Unigine::CallbackBase *endGameEvent = nullptr; bool isCounting = true; int physicalObjectsNum; Unigine::WidgetLabelPtr widget_timer, widget_goal; Unigine::ObjectTextPtr endText; };LevelManager.cpp (С++)#include "LevelManager.h" using namespace Unigine; using namespace Math; REGISTER_COMPONENT(LevelManager); void LevelManager::init() { LevelManager::initGUI(); // find the object text node of the widget endText = checked_ptr_cast<ObjectText>(Game::getPlayer()->findNode("header_text", 1)); // count dynamic objects in the level physicalObjectsNum = node->getNumChildren(); } void LevelManager::initGUI() { // get a GUI pointer GuiPtr gui = Gui::getCurrent(); // create a label widget and set up its parameters widget_timer = WidgetLabel::create(gui, "Time Left:"); widget_timer->setPosition(10, 10); widget_timer->setFontColor(vec4_red); widget_goal = WidgetLabel::create(gui, "Objects Left: "); widget_goal->setPosition(10, 30); widget_goal->setFontColor(vec4_blue); // add widgets to the GUI gui->addChild(widget_timer, Gui::ALIGN_OVERLAP); gui->addChild(widget_goal, Gui::ALIGN_OVERLAP); } void LevelManager::update() { // decrease the timer if (isCounting) { timer = timer - Game::getIFps(); if (timer <= 0) { //set end game text if (endText) endText->setText("Game Over"); if (endGameEvent) endGameEvent->run(); isCounting = false; } } // show the current time and objects left to clear if (isCounting) { widget_timer->setText(String::format("Time Left: %.2f s", timer.get())); widget_goal->setText(String::format("Objects Left: %d", physicalObjectsNum)); } //hide the widgets on endgame else { widget_timer->setEnabled(false); widget_goal->setEnabled(false); } //win if (physicalObjectsNum <= 0) { if (endText) endText->setText("Success!"); if (endGameEvent) endGameEvent->run(); isCounting = false; } } void LevelManager::shutdown() { widget_timer.deleteLater(); widget_goal.deleteLater(); } void LevelManager::decPhysicalObjectsNum() { physicalObjectsNum--; } - Switch back to UnigineEditor and create a new Dummy Node called level_manager and place it somewhere in the world.切换回 UnigineEditor 并创建一个名为 level_manager 的新 Dummy Node 并将其放置在世界某处。
-
Add a LevelManager component to the level_manager node via the Parameters window in the UnigineEditor.通过 UnigineEditor 中的 Parameters 窗口将 LevelManager 组件添加到 level_manager 节点。
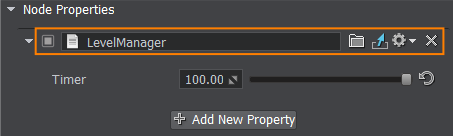
We created the system GUI via the API from the code. The alternative method is to use UI files.我们通过 代码中的 API 创建了系统 GUI。 另一种方法是使用 UI 文件。
Step 2. Detect Physical Objects步骤2。检测物理对象#
Only the level_manager's children nodes shall be deleted by the Kill Zone's trigger. Let's add each physical object that we created earlier as a child to the level_manager node. For the rules to function properly you also need to add a new condition and a method call to the KillZone component that checks if the entered node has a parent with the LevelManager component attached.只有 level_manager 的子节点会被 Kill Zone 的触发器删除。 让我们将 之前创建的每个物理对象 作为子节点添加到 level_manager 节点。 为了使规则正常运行,您还需要向 KillZone 组件添加一个新条件和一个方法调用,以检查输入的节点是否具有附加了LevelManager 组件的父节点。
-
Open the KillZone component in your IDE, add a levelManager field and replace the content of the Enter callback function according to the following code.在你的 IDE 中打开 KillZone 组件,添加一个 levelManager 字段并替换 Enter callback 函数根据以下代码。
KillZone.h (C++)#pragma once #include <UnigineComponentSystem.h> #include <UnigineWorlds.h> //========================== NEW - BEGIN =============================== #include "LevelManager.h" //=========================== NEW - END ================================ class KillZone : public Unigine::ComponentBase { public: // declare constructor and destructor for our class and define a property name. COMPONENT_DEFINE(KillZone, ComponentBase) // declare methods to be called at the corresponding stages of the execution sequence COMPONENT_INIT(init); protected: void init(); void enterEventHandler(const Unigine::NodePtr &target); private: // the area into which an object should fall Unigine::WorldTriggerPtr trigger; //========================== NEW - BEGIN =============================== LevelManager *levelManager; //=========================== NEW - END ================================ };KillZone.cpp (C++)#include "KillZone.h" using namespace Unigine; REGISTER_COMPONENT(KillZone); void KillZone::init() { trigger = checked_ptr_cast<WorldTrigger>(node); // subscribe for the Enter event (when an object enters the area) if (trigger) trigger->getEventEnter().connect(this, &KillZone::enterEventHandler); } void KillZone::enterEventHandler(const NodePtr &target) { //========================== NEW - BEGIN =============================== levelManager = getComponentInParent<LevelManager>(target); // check if the parent node has a LevelManager component attached if (levelManager) { // delete the entered node and decrease the amount of physical objects levelManager->decPhysicalObjectsNum(); target.deleteLater(); } //=========================== NEW - END ================================ } -
Let's set the level_manager node as a parent to physical objects. Open the ObjectGenerator component in your IDE and replace the code in the corresponding files with the following. Save the code in your IDE, build and run the solution to regenerate a property file for the component and switch back to UnigineEditor.让我们设置level_manager节点作为一个家长物理对象。在IDE中打开ObjectGenerator组件和替换的代码与下列相应的文件。保存您的IDE中的代码,构建和运行的解决方案组件和再生一个属性文件切换回UnigineEditor。
ObjectGenerator.h (C++)#include <UnigineComponentSystem.h> #include <UnigineGame.h> #pragma once class ObjectGenerator : public Unigine::ComponentBase { public: COMPONENT_DEFINE(ObjectGenerator, ComponentBase); COMPONENT_INIT(init, 1); // 1st initialization order //========================== NEW - BEGIN =============================== PROP_PARAM(Node, levelManager); //=========================== NEW - END ================================ protected: void init(); };ObjectGenerator.cpp (C++)#include "ObjectGenerator.h" #include <UniginePrimitives.h> using namespace Unigine; REGISTER_COMPONENT(ObjectGenerator); void ObjectGenerator::init() { //========================== NEW - BEGIN =============================== if (levelManager) { //=========================== NEW - END ================================ // cube ObjectMeshDynamicPtr box = Primitives::createBox(Math::vec3(1.0f)); //========================== NEW - BEGIN =============================== box->setParent(levelManager); //========================== NEW - END =============================== box->setTriggerInteractionEnabled(1); box->setIntersection(1, 0); box->setIntersectionMask(0x00000080, 0); // check the BulletIntersection bit box->setWorldTransform(translate(Math::Vec3(0.5f, 7.5f, 1.0f))); box->setMaterialPath("materials/mesh_base_0.mat", "*"); box->setName("box"); Unigine::BodyRigidPtr bodyBox = BodyRigid::create(box); ShapeBoxPtr shapeBox = ShapeBox::create(bodyBox, Math::vec3(1.0f)); ShapeSphere::create(bodyBox, 0.5f); bodyBox->setShapeBased(0); bodyBox->setMass(2.0f); // sphere ObjectMeshDynamicPtr sphere = Primitives::createSphere(0.5f, 9, 32); //========================== NEW - BEGIN =============================== sphere->setParent(levelManager); //========================== NEW - END =============================== sphere->setTriggerInteractionEnabled(1); sphere->setIntersection(1, 0); sphere->setIntersectionMask(0x00000080, 0); // check the BulletIntersection bit sphere->setWorldTransform(translate(Math::Vec3(4.5f, 5.5f, 1.0f))); sphere->setMaterialPath("materials/mesh_base_1.mat", "*"); sphere->setName("sphere"); BodyRigidPtr bodySphere = BodyRigid::create(sphere); ShapeSphere::create(bodySphere, 0.5f); bodySphere->setShapeBased(0); bodySphere->setMass(2.0f); // capsule ObjectMeshDynamicPtr capsule = Primitives::createCapsule(0.5f, 1.0f, 9, 32); //========================== NEW - BEGIN =============================== capsule->setParent(levelManager); //========================== NEW - END =============================== capsule->setTriggerInteractionEnabled(1); capsule->setIntersection(1, 0); capsule->setIntersectionMask(0x00000080, 0); // check the BulletIntersection bit capsule->setWorldTransform(translate(Math::Vec3(4.5f, 0.5f, 3.0f))); capsule->setMaterialPath("materials/mesh_base_2.mat", "*"); capsule->setName("capsule"); BodyRigidPtr bodyCapsule = BodyRigid::create(capsule); ShapeCapsule::create(bodyCapsule, 0.5f, 1.0f); bodyCapsule->setShapeBased(0); bodyCapsule->setMass(2.0f); //========================== NEW - BEGIN =============================== } //=========================== NEW - END ================================ } -
Select the object_generator node in the World Nodes window and drag the level_manager node to the corresponding field of the ObjectGenerator property.选择object_generator节点World Nodes窗口拖动level_manager节点的对应字段ObjectGenerator财产。
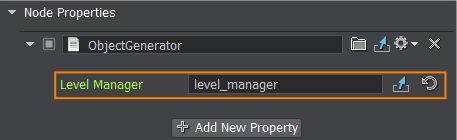
- Save changes to the world. Go to File->Save World or press Ctrl+S hotkey.保存更改。去File->Save World或者按Ctrl+S热键。
- Switch to your IDE. Save changes to the solution and then build and run the game to see the game rules in action.切换到您的IDE。保存更改到解决方案,然后构建和运行游戏的游戏规则。
本页面上的信息适用于 UNIGINE 2.18.1 SDK.
