Plugin Class
You can get access to the main loop of the Unigine engine by overriding virtual methods of the Unigine.Plugin class. This article describes the sample located in the <UnigineSDK>/source/csharp/samples/Api/Systems/Ffp/ directory.
See also
- An example can be found in the <UnigineSDK>/source/csharp/samples/Api/Systems/Ffp/ directory.
- C++ API classes Unigine::Plugin and Unigine::Ffp which have the same methods and behavior as in the C# API.
Plugin Class Usage Example
C# Side
To use the Unigine.Plugin class, you should create your own class and inherit it from the Unigine.Plugin class and override necessary methods, which the engine will perform in its main loop.
using System;
using Unigine;
/*
*/
class UnigineApp {
/*
*/
class FfpPlugin : Plugin {
private float time;
public override void gui() {
App app = App.get();
time += app.getIFps();
render(time);
}
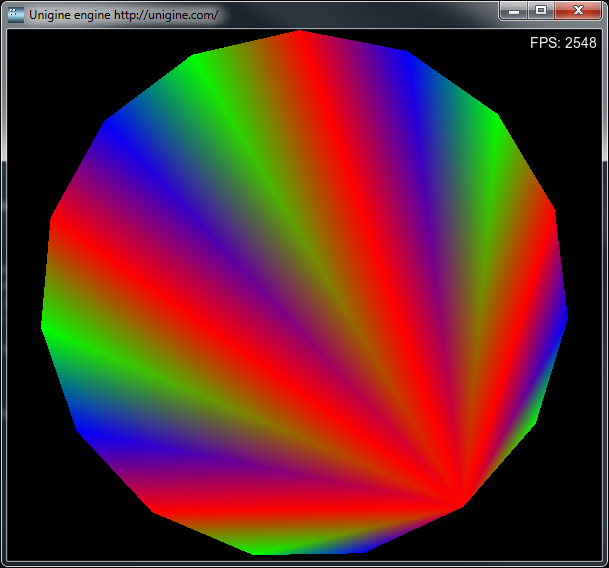
private void render(float time) {
App app = App.get();
Ffp ffp = Ffp.get();
// screen size
int width = app.getWidth();
int height = app.getHeight();
float radius = height / 2.0f;
ffp.enable(Ffp.MODE_SOLID);
ffp.setOrtho(width,height);
// begin triangles
ffp.beginTriangles();
// vertex colors
uint[] colors = { 0xffff0000, 0xff00ff00, 0xff0000ff };
// create vertices
int num_vertex = 16;
for(int i = 0; i < num_vertex; i++) {
float angle = MathLib.PI2 * i / (num_vertex - 1) - time;
float x = width / 2 + (float)Math.Sin(angle) * radius;
float y = height / 2 + (float)Math.Cos(angle) * radius;
ffp.addVertex(x,y);
ffp.setColor(colors[i % 3]);
}
// create indices
for(int i = 1; i < num_vertex; i++) {
ffp.addIndex(0);
ffp.addIndex(i);
ffp.addIndex(i - 1);
}
// end triangles
ffp.endTriangles();
ffp.disable();
}
}
/*
*/
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args) {
// initialize wrapper
Wrapper.init();
// initialize engine
Engine engine = Engine.init(Engine.VERSION,args);
// create plugin
FfpPlugin plugin = new FfpPlugin();
engine.addPlugin(plugin);
// enter main loop
engine.main();
// remove plugin
engine.removePlugin(plugin);
// shutdown engine
Engine.shutdown();
}
}In this part of the code we create the FfpPlugin class which inherits the Plugin class and override the gui() method. We specified the render() method and call it inside the overridden gui() method. Engine calls this function before gui each render frame.
In the Main() method, we create an instance of the FfpPlugin class and add it to the engine by using the addPlugin() method after the wrapper and the engine had been initialized.
Unigine Script Side
All the logic is implemented in the C# Ffp.cs file. There is only one command in the UnigineScript ffp.cpp file to show a console:
int init() {
// show console
engine.console.setActivity(1);
return 1;
}Output
The following result will be shown: