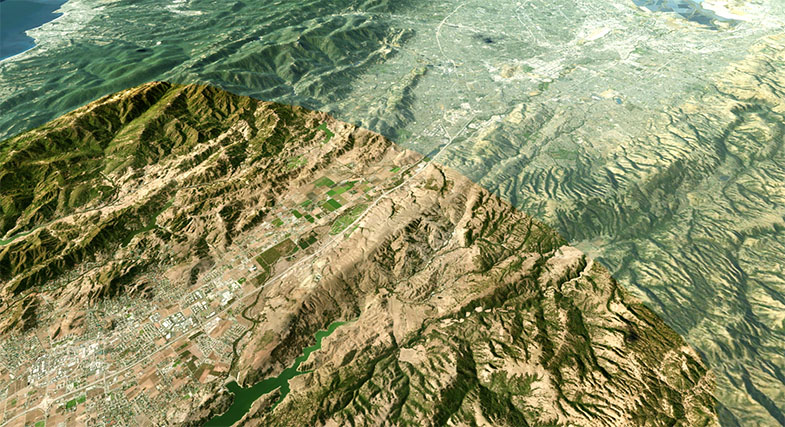
Sandworm (Experimental)
The Sandworm tool is used to generate georeferenced landscape of any form using the provided data sources. This tool helps to quickly re-create portions of the real world by projecting them onto a flat Landscape Terrain Object. The maximum size of the landscape depends on the available memory and data density, but normally it's enough to create a landscape of a big city or a country.
Placing world objects to their real world positions (latitude, longitude, and altitude) can be done via GeodeticsPlugin.
Sandworm generates a landscape using height map (elevation) and albedo (imagery) data provided. You can use the following types of data sources:
- Offline — locally stored tilesets: raster (elevation, imagery, and masks) and vector data sources from your local storage device
- Online — Tile Map Services (TMS): you can connect to both, open services (such as OpenStreetMap or various state/municipal databases) or private tile servers created and supported by users on the basis of services similar to QGIS (currently supported data from online sources: imagery and elevation).
Geo-referenced imagery and elevation data are processed using the GDAL — Geospatial Data Abstraction Library. It supports various raster formats with different map projections for input data. It is also possible to combine different projection types and data sources to generate a landscape.
The following formats of the data sources are supported:
- RGB and RGBA formats for albedo (imagery) data. Alpha-channel in the second case is used to mark no data areas.
- R format for height maps (elevation sources).
- R and RGBA formats for masks (landcover sources).
Bitness of the input formats can be 8, 16, or 32f.
GIS data sources can be used for generation of vegetation (raster data), buildings, landmarks, etc. (vector data):
- On the basis of landcover data, which is used for masking, Sandworm places vegetation.
- On the basis of vector data, procedural placement of other objects (buildings, landmarks, etc.) is done.
These data sources usually contain a lot of information that can be tagged and filtered using attribute filters.
Tags represent a color (color range) or an attribute value (range of values) and are used to filter the data necessary for generation of certain landcover areas or objects of the cultural layer (buildings). For each tag, you can specify a set of attribute filters to select certain data from the data source. You can specify as many filters as you need for each tag. The tags are used for objects placement on the landscape. For example, by using tags, you can:
- Generate grass or trees for areas marked with certain colors of the landcover texture.
- Generate buildings of a certain type only (e.g., apartments, garages, single- or multi-storey buildings, depending on the data stored in the vector data source).
Sandworm supports multiple data layers aligned by geo or raster coordinates: you can easily create high-resolution insets by adding a high-detailed landscape area over a low-detailed one. This can be useful for flight simulators, where high details are required only for areas around airports. The quality of generated landscape is determined by the density of the data sources used.
See Also#
- Article on Landscape Terrain
- Documentation on the GDAL library
- Wikipedia article on Equirectangular projection