Unigine语言对象符号(ULON)
ULON (Unigine Language Object Notation) is a universal format used in UNIGINE to describe complex structures similar to classes in Object-Oriented Programming. Landscape Terrain brushes as well as some of UNIGINE built-in materials are described using ULON. ULON(统一语言对象表示法)是UNIGINE中用于描述类似于面向对象编程中的类的复杂结构的通用格式。使用ULON描述了Landscape Terrain画笔以及一些UNIGINE内置材料。
The Engine supports loading and parsing files containing ULON-declarations, but does not support saving ULON-based structures to a file as such declarations are treated more like source code.引擎支持加载和解析包含ULON声明的文件,但是不支持将基于ULON的结构保存到文件中,因为这样的声明更像源代码。
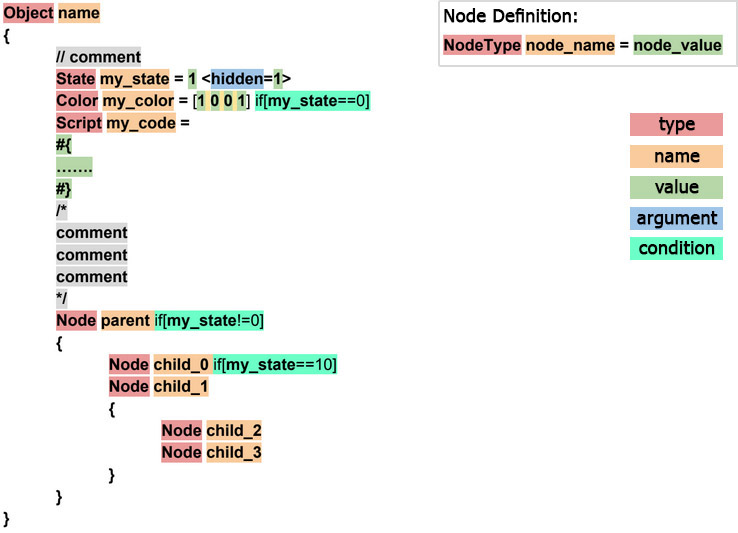
ULON Description Example ULON说明示例
See Also也可以看看#
Nodes节点数#
The basic element (building brick) of ULON is called a node. Each node has a type, a name, and a value. ULON的基本元素(建筑用砖)称为节点。每个节点都有一个类型(type),一个名称(name)和一个 值(value) 。
The following construct is used to declare a node:以下构造用于声明节点:

Both node name and type are written as strings:
Here is an example:
"Node Type" "node name" = node_value
NodeType node_name1 = node_value
- either a quoted string with standard escape characters,带有标准转义字符的带引号的字符串,
- or a bare word, beginning with a lower case letter, containing only letters, digits, and underscores "_".或裸词,以小写字母开头,仅包含字母,数字和下划线"_"。
"Node Type" "node name" = node_value
NodeType node_name1 = node_valueNode declarations can be nested, thus forming a hierarchy. So a node can have a parent and an unlimited number children.
Node parent
{
Node child_0
Node child_1
{
Node child_2
Node child_3
}
}
Node parent
{
Node child_0
Node child_1
{
Node child_2
Node child_3
}
}Values价值观#
ULON node values can be of the following types:
Boolean
Node my_node = true
Boolean
Node my_node = true
Node my_node = 1234
Integer number
Node my_node = 1234
Node my_node = 3.1459
Floating-point number
Node my_node = 3.1459
Quoted string with standard escape characters:
Node node = "word word"Quoted string with standard escape characters:
Node node = "word word"
Node node = word1_word2 Bare word, beginning with a lower case letter, containing only letters, digits, and underscores "_":
Node node = word1_word2
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}Heredoc string enclosed in #{ ... #}. This type can be used for code fragments (e.g., shader code embedded into material description):
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}
Node node = "word word"Bare word, beginning with a lower case letter, containing only letters, digits, and underscores "_":
Node node = word1_word2 Heredoc string enclosed in #{ ... #}. This type can be used for code fragments (e.g., shader code embedded into material description):
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}String
Node node = "word word"Quoted string with standard escape characters:
Node node = "word word"
Node node = word1_word2 Bare word, beginning with a lower case letter, containing only letters, digits, and underscores "_":
Node node = word1_word2
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}Heredoc string enclosed in #{ ... #}. This type can be used for code fragments (e.g., shader code embedded into material description):
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}
Node my_node = [100, 0.2, str str "str str str", #{vec4 asd = vec4_zero;#}]
This array has the following 6 elements:
Array containing a finite number of integer, float, and string elements
Node my_node = [100, 0.2, str str "str str str", #{vec4 asd = vec4_zero;#}]
This array has the following 6 elements:
Node my_node = true
Integer number
Node my_node = 1234
Floating-point number
Node my_node = 3.1459
String
Quoted string with standard escape characters:
Node node = "word word"Quoted string with standard escape characters:
Node node = "word word"
Node node = word1_word2 Bare word, beginning with a lower case letter, containing only letters, digits, and underscores "_":
Node node = word1_word2
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}Heredoc string enclosed in #{ ... #}. This type can be used for code fragments (e.g., shader code embedded into material description):
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}
Node node = "word word"Bare word, beginning with a lower case letter, containing only letters, digits, and underscores "_":
Node node = word1_word2 Heredoc string enclosed in #{ ... #}. This type can be used for code fragments (e.g., shader code embedded into material description):
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}Array containing a finite number of integer, float, and string elements
Node my_node = [100, 0.2, str str "str str str", #{vec4 asd = vec4_zero;#}]
This array has the following 6 elements:
ULON节点值可以是以下类型:
- Boolean
Node my_node = true 布尔值
_ Node my_node = true - Integer number
Node my_node = 1234 整数编号
_ Node my_node = 1234 - Floating-point number
Node my_node = 3.1459 浮点数
_ Node my_node = 3.1459 - String
- Quoted string with standard escape characters:
Node node = "word word"Quoted string with standard escape characters:
Node node = "word word" - Bare word, beginning with a lower case letter, containing only letters, digits, and underscores "_":
Node node = word1_word2 Bare word, beginning with a lower case letter, containing only letters, digits, and underscores "_":
Node node = word1_word2 - Heredoc string enclosed in #{ ... #}. This type can be used for code fragments (e.g., shader code embedded into material description):
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}Heredoc string enclosed in #{ ... #}. This type can be used for code fragments (e.g., shader code embedded into material description):
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}
Node node = "word word"Bare word, beginning with a lower case letter, containing only letters, digits, and underscores "_":
Node node = word1_word2 Heredoc string enclosed in #{ ... #}. This type can be used for code fragments (e.g., shader code embedded into material description):
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#} 字符串
- Quoted string with standard escape characters:
Node node = "word word"带标准转义字符的带引号的字符串:
Node node = "word word" - Bare word, beginning with a lower case letter, containing only letters, digits, and underscores "_":
Node node = word1_word2 裸词,以小写字母开头,仅包含字母,数字和下划线"_":
Node node = word1_word2 - Heredoc string enclosed in #{ ... #}. This type can be used for code fragments (e.g., shader code embedded into material description):
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}包含在#{ ... #}中的Heredoc字符串。此类型可用于代码片段(例如,嵌入到材质描述中的着色器代码):
Node my_node = #{C++ C# USC HLSL GLSL USSL#}
- Quoted string with standard escape characters:
- Array containing a finite number of integer, float, and string elements
Node my_node = [100, 0.2, str str "str str str", #{vec4 asd = vec4_zero;#}]
This array has the following 6 elements:- 100
- 0.2
- str
- str
- str str str
- vec4 asd = vec4_zero;
Node my_node = [100, 0.2, str str "str str str", #{vec4 asd = vec4_zero;#}] 该数组具有以下 6 元素:- 100
- 0.2
- str
- str
- str str str
- vec4 asd = vec4_zero;
Arguments争论#
ULON argument is a name - value pair (name = value). Arguments are additional parameters that can be associated with ULON nodes and used for various purposes (e.g. to define a tooltip or a title for a material parameter declaration). Arguments are enclosed in angle brackets < > and can be separated using "\t","\n","\r", as well as commas and spaces. ULON 参数是一个名称-值对(名称=值)。参数是可以与ULON节点关联并用于各种目的的其他参数(例如,为材料参数声明定义工具提示或标题)。参数包含在尖括号< >中,可以使用“ \ t”,“ \ n”,“ \ r”以及逗号和空格分隔。
Example: 示例:
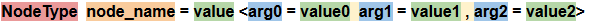
Conditions条件#
For each node a logical condition can be specified, if the condition fails the ULON node with all its children is ignored. Thus you can dynamically build the hierarchy of ULON nodes with a great degree of flexibility. This can be useful when the contents of the node depends on certain parameters, e.g. a shader to be used is defined by the rendering pass.
Condition of the parent node is added to the condition of the child: (parent_conditon) && (child_conditon)父节点的条件添加到子节点的条件:(parent_conditon) && (child_conditon)
Example:
Node parent if[var1 == 10 || var1 == 5]
{
Node child_0 if[var2 == 3]
Node child_1 if[var2 == 4]
{
Node child_2 if[var3 != 11]
Node child_3 if[var3 != 25]
}
}
示例:
Node parent if[var1 == 10 || var1 == 5]
{
Node child_0 if[var2 == 3]
Node child_1 if[var2 == 4]
{
Node child_2 if[var3 != 11]
ode child_3 if[var3 != 25]
}
}- parent condition: (var1 == 10 || var1 == 5)
- child_0 condition: (var1 == 10 || var1 == 5) && (var2 == 3)
- child_1 condition: (var1 == 10 || var1 == 5) && (var2 == 4)
- child_2 condition: (var1 == 10 || var1 == 5) && (var2 == 4) && (var3 != 11)
- child_3 condition: (var1 == 10 || var1 == 5) && (var2 == 4) && (var3 != 25)
Comments评论#
Adding comments make object declaration easier to understand, especially if the object is a complex one. The following type os comments are supported:添加注释使对象声明更易于理解,尤其是在对象是复杂对象的情况下。支持以下类型的os注释:
- single-line comments starting with "//":
// This is a single-line comment 单行以"//"开头的注释:
// This is a single-line comment - multi-line comments enclosed within "/*" and "*/":
/* This is
a multi-line
comment */ 包含在 "/*"和"*/"内的多行注释:
/* This is
a multi-line
comment */
