Enabling Selective Surface-Based Collision
Warning
The scope of applications for UnigineScript is limited to implementing materials-related logic (material expressions, scriptable materials, brush materials). Do not use UnigineScript as a language for application logic, please consider C#/C++ instead, as these APIs are the preferred ones. Availability of new Engine features in UnigineScript (beyond its scope of applications) is not guaranteed, as the current level of support assumes only fixing critical issues.
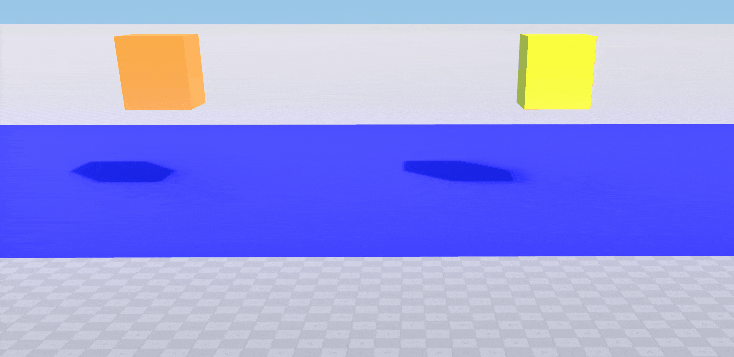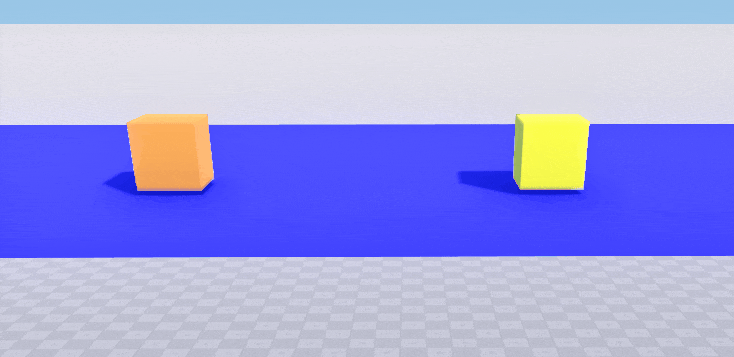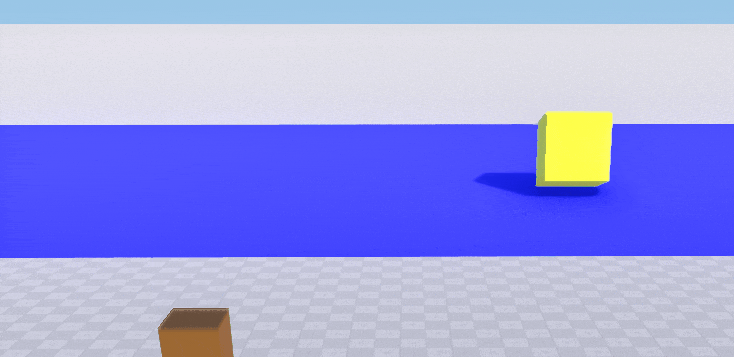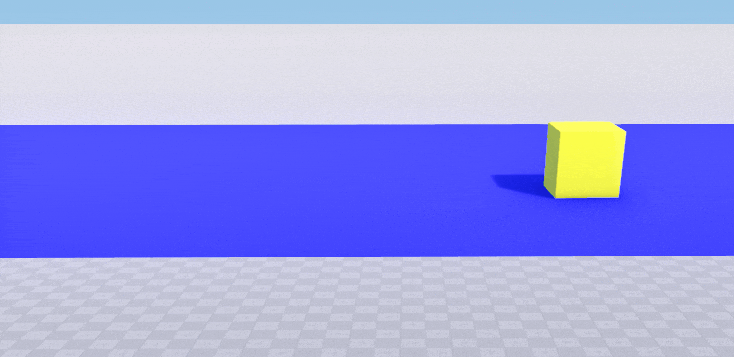
Surface-based collision using collision masks
This example shows how to enable collision detection for a surface using bitmasks. Two boxes (orange and yellow), each with a body and a box shape assigned, and a blue plane are created. We want the yellow box to collide with the surface of the blue plane and the orange box to pass through. So we set the following collision masks for the shapes of the boxes and for the surface of the plane.
| Element | Mask |
|---|---|
| Yellow box: shape | 0010 |
| Orange box: shape | 0001 |
| Plane: surface | 0010 |
Notice
Surface-to-surface collisions cannot be enabled using collision masks.
Source code (UnigineScript)
ObjectMeshStatic box1;
ObjectMeshStatic box2;
ObjectMeshStatic plane;
/// function, creating a named box of a specified size and color at pos
int create_box(Object &OM, string name, Vec4 color, Vec3 size, Vec3 pos)
{
// creating an auxiliary mesh with a box surface
Mesh meshbox = new Mesh();
meshbox.addBoxSurface("box_surface", size);
// creating a static mesh object using an auxiliary mesh and setting parameters
OM = new ObjectMeshStatic(meshbox);
OM.setWorldTransform(translate(pos));
OM.setMaterialParameterFloat4("albedo_color", color, 0);
OM.setCollision(1, 0);
OM.setName(name);
// assigning a rigid body with our object
BodyRigid body = class_remove(new BodyRigid(OM));
// creating a box shape and assigning it to the rigid body of our object
ShapeBox shape = class_remove(new ShapeBox(size));
body.addShape(shape,translate(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
// deleting the auxiliary mesh
delete meshbox;
return 1;
}
/// function, creating a named plane having a specified width and height at pos
int create_plane(Object &OM, string name, double width, double height, Vec3 pos)
{
// creating an auxiliary mesh with a plane surface
Mesh meshplane = new Mesh();
meshplane.addPlaneSurface("plane_surface", width, height, 1.0f);
// creating a static mesh object using an auxiliary mesh and setting parameters
OM = new ObjectMeshStatic(meshplane);
OM.setWorldTransform(translate(pos));
OM.setMaterialParameterFloat4("albedo_color", Vec4(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f), 0);
OM.setCollision(1, 0);
OM.setName(name);
// deleting the auxiliary mesh
delete meshplane;
return 1;
}
int init() {
// setting up a player
Player player = new PlayerSpectator();
player.setPosition(Vec3(0.0f, -6.0f, 12.5f));
player.setDirection(Vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, -0.4f));
engine.game.setPlayer(player);
// creating a scene: two boxes and a plane
create_box(box1, "Box 1", Vec4(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), Vec3(0.5f), Vec3(1.5f, 0.0f, 12.0f));
create_box(box2, "Box 2", Vec4(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.1f, 1.0f), Vec3(0.5f), Vec3(-1.5f, 0.0f, 12.0f));
create_plane(plane, "Plane", 10.0f, 6.0f, Vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 10.5f));
// setting shape collision mask for the first box [00000000000000000000000000000010]
box1.getBody().getShape(0).setCollisionMask(2);
// setting shape collision mask for the second box [00000000000000000000000000000001]
box2.getBody().getShape(0).setCollisionMask(1);
// setting collision mask for the plane surface [00000000000000000000000000000010]
plane.setCollisionMask(2, 0);
return 1;
}
int shutdown() {
// memory cleanup
delete box1;
delete box2;
delete plane;
return 1;
}Last update:
2022-03-10
Help improve this article
Was this article helpful?
(or select a word/phrase and press Ctrl+Enter)