C# API Reference
Most functions and classes in C# API have the same names and behavior as in C++ API.
Special Aspects of Pointers#
You should take into account that each class of C# API has methods for managing pointers:
- refPtr() - returns the reference counter.
- getPtr() - returns the internal pointer.
- checkPtr() - returns false if the internal pointer is IntPtr.Zero ; otherwise, returns true.
- clearPtr() - clears the pointer. After calling clearPtr(), getPtr() will return IntPtr.Zero and checkPtr() will return false.
- destroyPtr() - destroys the pointer.
The pointers are managed in the same way as in C++.
Differences in Function Exporting#
To export your function from C# to UnigineScript, you should use Interpreter.Function() with different postfixes instead of MakeExternFunction(). The postfix of Function shows the number of arguments (up to 8 arguments) and the type of return value:
- no postfix - void.
- i - int.
- d - double.
- f - float.
- s - string.
- v - Unigine.Variable (the same class as the C++ API Unigine::Variable class).
See also an example of function exporting.
Renderer Class#
The C# API also has the Renderer class. This class allows you to get access to the specific pass of Rendering Sequence by overriding virtual methods of the Unigine.Renderer class.
You can get access to the existing renderer instance either by using get() function:
/* ... */
// get existing instance of the Renderer
Renderer renderer = Renderer.get();
/* ... */Or by referring to the variable of the Engine class:
/* ... */
// get existing instance of the Renderer
Renderer renderer = Engine.renderer;
/* ... */Read about the C++ API Unigine::Renderer class which has the same methods and behavior as in the C# API.
Using References#
You can add your .dll libraries to the C# project to use specific structures, classes and methods. If you use Visual Studio you can add NuGet packages to your solution by clicking Project -> Manage NuGet Packages...
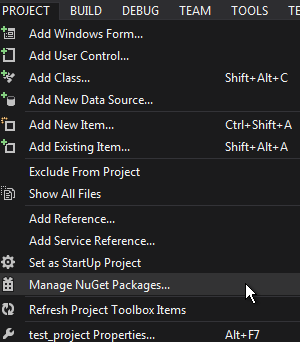
View Documentation by Using Visual Studio#
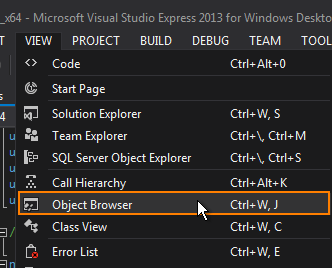
You can read the documentation of some of C# API methods by using the Object Browser in Visual Studio.
- In Visual Studio, click View -> Object Browser or press CTRL + W and then J.
The Object Browser window will open. The Object Browser displays three panes: an Objects pane on the left, a Members pane on the upper right, and a Description pane on the lower right.
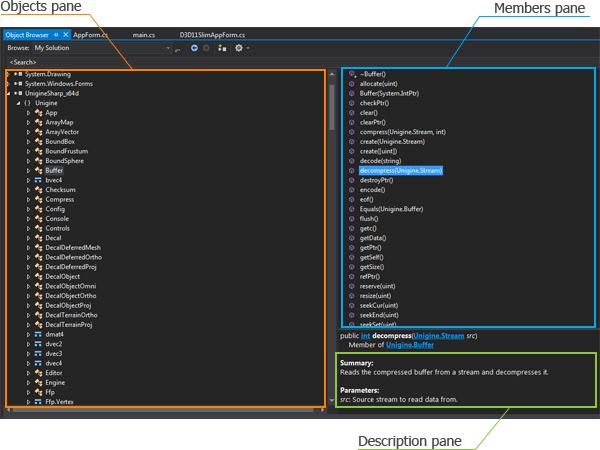
- Select the UnigineSharp_x64d (or UnigineSharp_x86d) object in the Object pane and choose the class you wish to view.
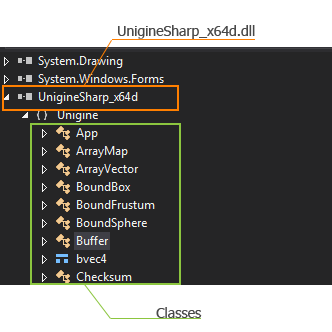
- Specify the member in the Members pane.
- If the description for chosen member exists, it will appear in the Description pane.
See Also#
- Article on C++ API Reference.